Reservoir competence of vertebrate hosts for Anaplasma phagocytophilum
- PMID: 23171835
- PMCID: PMC3557888
- DOI: 10.3201/eid1812.120919
Reservoir competence of vertebrate hosts for Anaplasma phagocytophilum
Abstract
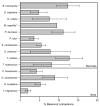
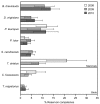
Fourteen vertebrate species (10 mammals and 4 birds) were assessed for their ability to transmit Anaplasma phagocytophilum, the bacterium that causes human granulocytic anaplasmosis, to uninfected feeding ixodid ticks. Small mammals were most likely to infect ticks but all species assessed were capable of transmitting the bacterium, in contrast to previous findings.
Figures
References
-
- Demma LJ, Holman RC, McQuiston JH, Krebs JW, Swerdlow DL. Epidemiology of human ehrlichiosis and anaplasmosis in the United States, 2001–2002. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2005;73:400–9. - PubMed
-
- Foley JE, Foley P, Brown RN, Lane RS, Dumler JS, Madigan JE. Ecology of granulocytic ehrlichiosis and Lyme disease in the western United States. J Vector Ecol. 2004;29:41–50. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
