Activity-regulated RNA editing in select neuronal subfields in hippocampus
- PMID: 23172290
- PMCID: PMC3553983
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gks1045
Activity-regulated RNA editing in select neuronal subfields in hippocampus
Abstract
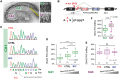
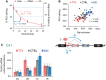
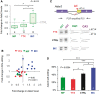
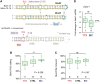
RNA editing by adensosine deaminases is a widespread mechanism to alter genetic information in metazoa. In addition to modifications in non-coding regions, editing contributes to diversification of protein function, in analogy to alternative splicing. However, although splicing programs respond to external signals, facilitating fine tuning and homeostasis of cellular functions, a similar regulation has not been described for RNA editing. Here, we show that the AMPA receptor R/G editing site is dynamically regulated in the hippocampus in response to activity. These changes are bi-directional, reversible and correlate with levels of the editase Adar2. This regulation is observed in the CA1 hippocampal subfield but not in CA3 and is thus subfield/celltype-specific. Moreover, alternative splicing of the flip/flop cassette downstream of the R/G site is closely linked to the editing state, which is regulated by Ca(2+). Our data show that A-to-I RNA editing has the capacity to tune protein function in response to external stimuli.
Figures
Comment on
- doi: 10.1093/nar/gks1044
References
-
- Jepson JE, Reenan RA. RNA editing in regulating gene expression in the brain. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 2008;1779:459–470. - PubMed
-
- Peng Z, Cheng Y, Tan BC, Kang L, Tian Z, Zhu Y, Zhang W, Liang Y, Hu X, Tan X, et al. Comprehensive analysis of RNA-Seq data reveals extensive RNA editing in a human transcriptome. Nat. Biotechnol. 2012;30:253–260. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

