Expression of the plant viral protease NIa in the brain of a mouse model of Alzheimer's disease mitigates Aβ pathology and improves cognitive function
- PMID: 23172351
- PMCID: PMC3538981
- DOI: 10.3858/emm.2012.44.12.082
Expression of the plant viral protease NIa in the brain of a mouse model of Alzheimer's disease mitigates Aβ pathology and improves cognitive function
Abstract
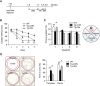
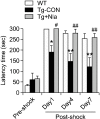
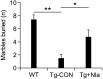
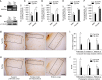
The plant viral protease, NIa, has a strict substrate specificity for the consensus sequence of Val-Xaa-His-Gln, with a scissoring property after Gln. We recently reported that NIa efficiently cleaved the amyloid-β (Aβ) peptide, which contains the sequence Val-His-His-Gln in the vicinity of the cleavage site by α-secretase, and that the expression of NIa using a lentiviral system in the brain of AD mouse model reduced plaque deposition levels. In the present study, we investigated whether exogenous expression of NIa in the brain of AD mouse model is beneficial to the improvement of cognitive deficits. To address this question, Lenti-NIa was intracerebrally injected into the brain of Tg-APPswe/ PS1dE9 (Tg-APP/PS1) mice at 7 months of age and behavioral tests were performed 15-30 days afterwards. The results of the water maze test indicated that Tg-APP/PS1 mice which had been injected with Lenti-GFP showed an increased latency in finding the hidden-platform and markedly enhanced navigation near the maze-wall, and that such behavioral deficits were significantly reversed in Tg-APP/PS1 mice injected with Lenti-NIa. In the passive avoidance test, Tg-APP/PS1 mice exhibited a severe deficit in their contextual memory retention, which was reversed by NIa expression. In the marble burying test, Tg-APP/PS1 mice buried marbles fewer than non-transgenic mice, which was also significantly improved by NIa. After behavioral tests, it was verified that the Tg-APP/PS1 mice with Lenti-NIa injection had reduced Aβ levels and plaque deposition when compared to Tg-APP/PS1 mice. These results showed that the plant viral protease, NIa, not only reduces Aβ pathology, but also improves behavioral deficits.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Cerebral inoculation of human A53T α-synuclein reduces spatial memory decline and amyloid-β aggregation in APP/PS1 transgenic mice of Alzheimer's disease.Brain Res Bull. 2018 Oct;143:116-122. doi: 10.1016/j.brainresbull.2018.10.003. Epub 2018 Oct 24. Brain Res Bull. 2018. PMID: 30366065
-
Conditional inactivation of presenilin 1 prevents amyloid accumulation and temporarily rescues contextual and spatial working memory impairments in amyloid precursor protein transgenic mice.J Neurosci. 2005 Jul 20;25(29):6755-64. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1247-05.2005. J Neurosci. 2005. PMID: 16033885 Free PMC article.
-
Soluble Aβ levels correlate with cognitive deficits in the 12-month-old APPswe/PS1dE9 mouse model of Alzheimer's disease.Behav Brain Res. 2011 Sep 23;222(2):342-50. doi: 10.1016/j.bbr.2011.03.072. Epub 2011 Apr 14. Behav Brain Res. 2011. PMID: 21513747
-
Using mice to model Alzheimer's dementia: an overview of the clinical disease and the preclinical behavioral changes in 10 mouse models.Front Genet. 2014 Apr 23;5:88. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2014.00088. eCollection 2014. Front Genet. 2014. PMID: 24795750 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Oleuropein aglycone and polyphenols from olive mill waste water ameliorate cognitive deficits and neuropathology.Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2017 Jan;83(1):54-62. doi: 10.1111/bcp.12993. Epub 2016 May 21. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2017. PMID: 27131215 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Inhibition of adenylyl cyclase type 5 prevents L-DOPA-induced dyskinesia in an animal model of Parkinson's disease.J Neurosci. 2014 Aug 27;34(35):11744-53. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0864-14.2014. J Neurosci. 2014. PMID: 25164669 Free PMC article.
-
An update of animal models of Alzheimer disease with a reevaluation of plaque depositions.Exp Neurobiol. 2013 Jun;22(2):84-95. doi: 10.5607/en.2013.22.2.84. Epub 2013 Jun 27. Exp Neurobiol. 2013. PMID: 23833557 Free PMC article.
-
Plant Viral Proteases: Beyond the Role of Peptide Cutters.Front Plant Sci. 2018 May 17;9:666. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2018.00666. eCollection 2018. Front Plant Sci. 2018. PMID: 29868107 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hyperoxygenation revitalizes Alzheimer's disease pathology through the upregulation of neurotrophic factors.Aging Cell. 2019 Apr;18(2):e12888. doi: 10.1111/acel.12888. Epub 2019 Feb 11. Aging Cell. 2019. PMID: 30746828 Free PMC article.
-
Longitudinal assessment of cognitive function in the APPswe/PS1dE9 mouse model of Alzheimer's-related beta-amyloidosis.Neurobiol Aging. 2023 Aug;128:85-99. doi: 10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2023.03.010. Epub 2023 Apr 2. Neurobiol Aging. 2023. PMID: 37120419 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Benilova I, Karran E, De Strooper B. The toxic Aβ oligomer and Alzheimer's disease: an emperor in need of clothes. Nat Neurosci. 2012;15:349–357. - PubMed
-
- Dahlgren KN, Manelli AM, Stine WB, Jr, Baker LK, Krafft GA, LaDu MJ. Oligomeric and fibrillar species of amyloid-beta peptides differentially affect neuronal viability. J Biol Chem. 2002;277:32046–32053. - PubMed
-
- Deacon RM. Digging and marble burying in mice: simple methods for in vivo identification of biological impacts. Nat Protoc. 2006;1:122–124. - PubMed
-
- Farris W, Mansourian S, Chang Y, Lindsley L, Eckman EA, Frosch MP, Eckman CB, Tanzi RE, Selkoe DJ, Guenette S. Insulin-degrading enzyme regulates the levels of insulin, amyloid beta-protein, and the beta-amyloid precursor protein intracellular domain in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2003;100:4162–4167. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
