Combination of multichannel single-voxel MRS signals using generalized least squares
- PMID: 23172656
- PMCID: PMC3582859
- DOI: 10.1002/jmri.23941
Combination of multichannel single-voxel MRS signals using generalized least squares
Abstract
Purpose: To propose using the generalized least square (GLS) algorithm for combining multichannel single-voxel magnetic resonance spectroscopy (MRS) signals.
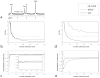
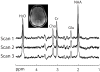
Materials and methods: Phantom and in vivo brain MRS experiments on a 7 T scanner equipped with a 32-channel receiver coil, as well as Monte Carlo simulations, were performed to compare the coefficient of variation (CV) of the GLS method with those of two recently reported spectral combination methods.
Results: Compared to the two existing methods, the GLS method significantly reduced CV values for the simulation, phantom, and in vivo experiments.
Conclusion: The GLS method can lead to improved precision of peak quantification.
Copyright © 2012 Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Figures


References
-
- Hyde JS, Jesmanowicz A, Froncisz W, Kneeland JB, Grist TM, Campagna NF. Parallel Image Acquisition from Noninteracting Local Coils. Journal of Magnetic Resonance. 1986;70(3):512–517.
-
- Roemer PB, Edelstein WA, Hayes CE, Souza SP, Mueller OM. The Nmr Phased-Array. Magnetic Resonance in Medicine. 1990;16(2):192–225. - PubMed
-
- Hardy CJ, Bottomley PA, Rohling KW, Roemer PB. An Nmr Phased-Array for Human Cardiac P-31 Spectroscopy. Magnetic Resonance in Medicine. 1992;28(1):54–64. - PubMed
-
- Wright SM, Wald LL. Theory and application of array coils in MR spectroscopy. Nmr in Biomedicine. 1997;10(8):394–410. - PubMed
-
- Prock T, Collins DJ, Dzik-Jurasz ASK, Leach MO. An algorithm for the optimum combination of data from arbitrary magnetic resonance phased array probes. Physics in Medicine and Biology. 2002;47(2):N39–N46. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

