Noncontrast-enhanced renal angiography using multiple inversion recovery and alternating TR balanced steady-state free precession
- PMID: 23172805
- PMCID: PMC4012072
- DOI: 10.1002/mrm.24480
Noncontrast-enhanced renal angiography using multiple inversion recovery and alternating TR balanced steady-state free precession
Abstract
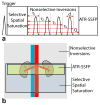
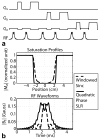
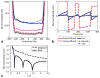
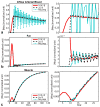
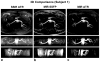
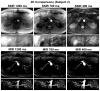
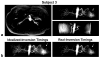
Noncontrast-enhanced renal angiography techniques based on balanced steady-state free precession avoid external contrast agents, take advantage of high inherent blood signal from the T 2 / T 1 contrast mechanism, and have short steady-state free precession acquisition times. However, background suppression is limited; inflow times are inflexible; labeling region is difficult to define when tagging arterial flow; and scan times are long. To overcome these limitations, we propose the use of multiple inversion recovery preparatory pulses combined with alternating pulse repetition time balanced steady-state free precession to produce renal angiograms. Multiple inversion recovery uses selective spatial saturation followed by four nonselective inversion recovery pulses to concurrently null a wide range of background T 1 species while allowing for adjustable inflow times; alternating pulse repetition time steady-state free precession maintains vessel contrast and provides added fat suppression. The high level of suppression enables imaging in three-dimensional as well as projective two-dimensional formats, the latter of which has a scan time as short as one heartbeat. In vivo studies at 1.5 T demonstrate the superior vessel contrast of this technique.
Keywords: SSFPangiography; angiography; multiple inversion recovery; noncontrast-enhanced angiography; projective imaging.
© 2012 Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Adaptive online self-gating (ADIOS) for free-breathing noncontrast renal MR angiography.Magn Reson Med. 2015 Jan;73(1):312-7. doi: 10.1002/mrm.25121. Epub 2014 Jan 29. Magn Reson Med. 2015. PMID: 24478221 Free PMC article.
-
Optimization of 4D vessel-selective arterial spin labeling angiography using balanced steady-state free precession and vessel-encoding.NMR Biomed. 2016 Jun;29(6):776-86. doi: 10.1002/nbm.3515. Epub 2016 Apr 13. NMR Biomed. 2016. PMID: 27074149 Free PMC article.
-
Improved renal perfusion measurement with a dual navigator-gated Q2TIPS fair technique.Magn Reson Med. 2010 Nov;64(5):1352-9. doi: 10.1002/mrm.22532. Magn Reson Med. 2010. PMID: 20593428 Free PMC article.
-
Non-contrast enhanced MR angiography: physical principles.J Magn Reson Imaging. 2012 Aug;36(2):286-304. doi: 10.1002/jmri.23641. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2012. PMID: 22807222 Review.
-
Non-contrast-enhanced MR imaging of renal artery stenosis at 1.5 tesla.Magn Reson Imaging Clin N Am. 2009 Feb;17(1):13-27. doi: 10.1016/j.mric.2009.01.002. Magn Reson Imaging Clin N Am. 2009. PMID: 19364597 Review.
Cited by
-
Use of Multiplied, Added, Subtracted and/or FiTted Inversion Recovery (MASTIR) pulse sequences.Quant Imaging Med Surg. 2020 Jun;10(6):1334-1369. doi: 10.21037/qims-20-568. Quant Imaging Med Surg. 2020. PMID: 32550142 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Safian RD, Textor SC. Renal-artery stenosis. N Engl J Med. 2001;344:431–442. - PubMed
-
- Prince MR, Narasimham DL, Stanley JC, Chenevert TL, Williams DM, Marx MV, Cho KJ. Breath-hold gadolinium-enhanced MR angiography of the abdominal aorta and its major branches. Radiology. 1995;197:785–792. - PubMed
-
- Hany TF, Debatin JF, Leung DA, Pfammatter T. Evaluation of the aortoiliac and renal arteries: comparison of breath-hold, contrast-enhanced, three-dimensional MR angiography with conventional catheter angiography. Radiology. 1997;204:357–362. - PubMed
-
- Schoenberg SO, Rieger J, Weber CH, Michaely HJ, Waggershauser T, Ittrich C, Dietrich O, Reiser MF. High-spatial-resolution MR angiography of renal arteries with integrated parallel acquisitions: comparison with digital subtraction angiography and US. Radiology. 2005;235:687–698. - PubMed
-
- Marckmann P, Skov L, Rossen K, Dupont A, Damholt MB, Heaf JG, Thomsen HS. Nephrogenic systemic fibrosis: suspected causative role of gadodiamide used for contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2006;17:2359–62. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

