Nicotine and insulin resistance: when the smoke clears
- PMID: 23172960
- PMCID: PMC3501863
- DOI: 10.2337/db12-1100
Nicotine and insulin resistance: when the smoke clears
Figures
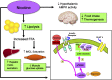
Comment on
-
Novel and reversible mechanisms of smoking-induced insulin resistance in humans.Diabetes. 2012 Dec;61(12):3156-66. doi: 10.2337/db12-0418. Epub 2012 Sep 10. Diabetes. 2012. PMID: 22966072 Free PMC article.
Similar articles
-
Novel and reversible mechanisms of smoking-induced insulin resistance in humans.Diabetes. 2012 Dec;61(12):3156-66. doi: 10.2337/db12-0418. Epub 2012 Sep 10. Diabetes. 2012. PMID: 22966072 Free PMC article.
-
Obesity Paradox and Smoking Gun: A Mystery of Statistical Confounding?Circ Res. 2018 Jun 8;122(12):1642-1644. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.118.312897. Circ Res. 2018. PMID: 29880498 Free PMC article.
-
Smoking induces insulin resistance--a potential link with the insulin resistance syndrome.J Intern Med. 1993 Apr;233(4):327-32. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2796.1993.tb00680.x. J Intern Med. 1993. PMID: 8463765 Clinical Trial.
-
Insulin resistance and compensatory hyperinsulinemia: the key player between cigarette smoking and cardiovascular disease?J Am Coll Cardiol. 2003 Mar 19;41(6):1044-7. doi: 10.1016/s0735-1097(02)02982-0. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2003. PMID: 12651055 Review.
-
Insulin resistance and coronary heart disease.Curr Opin Lipidol. 1996 Aug;7(4):217-26. doi: 10.1097/00041433-199608000-00008. Curr Opin Lipidol. 1996. PMID: 8883497 Review.
Cited by
-
Association between Self-Reported Smoking and Hemoglobin A1c in a Korean Population without Diabetes: The 2011-2012 Korean National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey.PLoS One. 2015 May 26;10(5):e0126746. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0126746. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26011526 Free PMC article.
-
Cardiovascular Risk Assessment Among People With Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus in Urban Slums of Central Karnataka, India.Cureus. 2023 Oct 8;15(10):e46687. doi: 10.7759/cureus.46687. eCollection 2023 Oct. Cureus. 2023. PMID: 37942395 Free PMC article.
-
Development and Validation of a Prevalence Model for Latent Autoimmune Diabetes in Adults (LADA) Among Patients First Diagnosed with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus (T2DM).Med Sci Monit. 2021 Sep 15;27:e932725. doi: 10.12659/MSM.932725. Med Sci Monit. 2021. PMID: 34521804 Free PMC article.
-
Longitudinal Analysis of Diabetes Mellitus Risk: Smoking Status and Smoking Cessation.J Clin Med. 2024 Jul 4;13(13):3927. doi: 10.3390/jcm13133927. J Clin Med. 2024. PMID: 38999492 Free PMC article.
-
Metabolomic Insights into Smoking-Induced Metabolic Dysfunctions: A Comprehensive Analysis of Lipid and Amino Acid Metabolomes.Metabolites. 2025 Feb 4;15(2):96. doi: 10.3390/metabo15020096. Metabolites. 2025. PMID: 39997721 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Willi C, Bodenmann P, Ghali WA, Faris PD, Cornuz J. Active smoking and the risk of type 2 diabetes: a systematic review and meta-analysis. JAMA 2007;298:2654–2664 - PubMed
-
- Chiolero A, Faeh D, Paccaud F, Cornuz J. Consequences of smoking for body weight, body fat distribution, and insulin resistance. Am J Clin Nutr 2008;87:801–809 - PubMed
-
- Hofstetter A, Schutz Y, Jéquier E, Wahren J. Increased 24-hour energy expenditure in cigarette smokers. N Engl J Med 1986;314:79–82 - PubMed

