A novel clinical indicator using cardiac technetium-99m sestamibi kinetics for evaluating cardiotoxicity in cancer patients treated with multiagent chemotherapy
- PMID: 23173103
- PMCID: PMC3499935
A novel clinical indicator using cardiac technetium-99m sestamibi kinetics for evaluating cardiotoxicity in cancer patients treated with multiagent chemotherapy
Abstract
Background: Multiagent chemotherapy (MCT) has mitochondrial targets. Since technetium-99m-sestamibi (MIBI) is a marker of mitochondrial metabolism, cardiac MIBI uptake and MIBI washout rate (%WR) may detect MCT-induced cardiotoxicity.
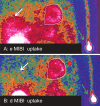
Methods: In 16 cancer patients on MCT for 10 months and in 14 non-cancer controls, cardiac MIBI uptake between early (30 min) and delayed (3 hours) post-injection planar images was measured as counts per pixel (cpp). The MIBI cardiac %WR was also measured.
Results: When MCT patients and controls were compared, early and cardiac delayed MIBI uptake were greater in MCT patients (45 ± 12 cpp vs. 30 ± 4 cpp; p <0.04) and (30 ± 8 cpp vs. 25 ± 2 cpp; p < 0.02), but % WR did not change (12 ± 4% vs. 13 ± 3%; p = ns). However, in the MCT patients, the MIBI cardiac %WR was more rapid because it was obtained at the same time as in the control patients but from a greater amount of MIBI cardiac uptake. On 36-months follow-up, only MCT patients died of cardiac death. Overall survival risk parameters, only delayed cardiac MIBI uptake (Odds ratio = 1.7, p<0.001) and early cardiac MIBI uptake (Odds ratio = 1.2, p<0.02) were found to be significantly associated with cardiac mortality.
Conclusions: In experimental studies, anticancer drugs elicit mitochondrial membrane hyperpolarization with passive cardiac MIBI uptake. In MCT patients, the increased cardiac MIBI uptake and rapid %WR compared with controls may reflect mitochondrial membrane dysfunction, pre-clinical cardiotoxicity and thus poor prognosis.
Keywords: Multiagent chemotherapy (MCT); cancer; cardiotoxicity; mitochondrial metabolism; multiagent chemotherapy; technetium-99m-sestamibi (MIBI).
Figures


Similar articles
-
A novel clinical indicator using Tc-99m sestamibi for evaluating cardiac mitochondrial function in patients with cardiomyopathies.J Nucl Cardiol. 2007 Apr;14(2):215-20. doi: 10.1016/j.nuclcard.2006.10.022. J Nucl Cardiol. 2007. PMID: 17386384
-
99mTc-MIBI SPET in non-small cell lung cancer in relationship with Pgp and prognosis.Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2002 Jul;29(7):876-81. doi: 10.1007/s00259-002-0804-7. Epub 2002 Apr 26. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2002. PMID: 12111127 Clinical Trial.
-
Tc-99m MIBI SPECT in prediction of prognosis in patients with small cell lung cancer.Ann Nucl Med. 2006 May;20(4):269-75. doi: 10.1007/BF02984643. Ann Nucl Med. 2006. PMID: 16856570 Clinical Trial.
-
Evaluation of Cardiac Mitochondrial Function by a Nuclear Imaging Technique using Technetium-99m-MIBI Uptake Kinetics.Asia Ocean J Nucl Med Biol. 2013 Spring;1(1):39-43. doi: 10.7508/aojnmb.2013.01.008. Asia Ocean J Nucl Med Biol. 2013. PMID: 27408841 Free PMC article. Review.
-
99mTc-MIBI Scintigraphy for the Preoperative Assessment of Histological Response to Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy in Patients With Osteosarcoma: A Systematic Review and a Bivariate Meta-Analysis.Front Oncol. 2020 May 22;10:762. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2020.00762. eCollection 2020. Front Oncol. 2020. PMID: 32528883 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Cardiac molecular pathways influenced by doxorubicin treatment in mice.Sci Rep. 2019 Feb 21;9(1):2514. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-38986-w. Sci Rep. 2019. PMID: 30792528 Free PMC article.
-
Detection of anthracycline-induced cardiotoxicity using perfusion-corrected 99mTc sestamibi SPECT.Sci Rep. 2019 Jan 18;9(1):216. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-36721-5. Sci Rep. 2019. PMID: 30659226 Free PMC article.
-
Noninvasive imaging of cardiovascular injury related to the treatment of cancer.JACC Cardiovasc Imaging. 2014 Aug;7(8):824-38. doi: 10.1016/j.jcmg.2014.06.007. JACC Cardiovasc Imaging. 2014. PMID: 25124015 Free PMC article. Review.
-
An update on cardio-oncology.Trends Cardiovasc Med. 2014 Oct;24(7):285-95. doi: 10.1016/j.tcm.2014.07.003. Epub 2014 Jul 22. Trends Cardiovasc Med. 2014. PMID: 25153017 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Bassily MN, Wilson R, Pompei F, Burmistrov D. Cancer survival as a function of age at diagnosis: A study of the Surveillance, Epidemiology and End Results database. Cancer Epidemiol. 2010;34:667–681. - PubMed
-
- Torrisi JM, Schwartz LH, Gollub MJ, Ginsberg MS, Bosl GJ, Hricak H. CT findings of chemotherapy-induced toxicity: what radiologists need to know about the clinical and radiologic manifestations of chemotherapy toxicity. Radiology. 2011;258:41–56. - PubMed
-
- Frezza C, Gottlieb E. Mitochondria in cancer: Not just innocent bystanders. Semin Cancer Biol. 2009;19:411. - PubMed
-
- Crane P, Laliberté R, Heminway S, Thoolen M, Orlandi C. Effect of mitochondrial viability and metabolism on technetium-99m-sestamibi myocardial retention. Eur J Nucl Med. 1993;20:20–25. - PubMed
-
- Fukushima K, Momose M, Kondo C, Higuchi T, Kusakabe K, Hagiwara N. Myocardial 99mTcsestamibi extraction and washout in hypertensive heart failure using an isolated rat heart. Nucl Med Biol. 2010;37:1005–1012. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
