Are keloid and hypertrophic scar different forms of the same disorder? A fibroproliferative skin disorder hypothesis based on keloid findings
- PMID: 23173565
- PMCID: PMC7950391
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1742-481X.2012.01118.x
Are keloid and hypertrophic scar different forms of the same disorder? A fibroproliferative skin disorder hypothesis based on keloid findings
Abstract
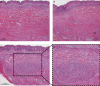
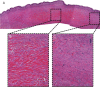
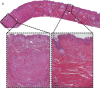
Hypertrophic scars (HSs) and keloids are commonly seen as two different diseases by both clinicians and pathologists. However, as supported by histological evidence showing they share increased numbers of fibroblasts and accumulate collagen products, HS and keloid might be different forms of the same pathological entity, rather than separate conditions. To test this hypothesis, keloids from patients who underwent scar excisions (n = 20) in Nippon Medical School from 2005 to 2010 were examined histologically. The proportion and distribution of cellular and matrix collagen components were evaluated at the centre and periphery of each sample. In keloid samples, coexistence of hyalinised collagen, which is the most important pathognomonic characteristic of a keloid and dermal nodules that are considered to be characteristic of HS, was found. Moreover, hyalinised fibres appeared to initiate from the corner of the dermal nodules. Key features of inflammation such as microvessels, fibroblasts and inflammatory cells all decreased gradually from the periphery to the centre of keloids, indicative of reduced inflammation in the centre. Thus, we hypothesise that HS and keloid can be considered as successive stages of the same fibroproliferative skin disorder, with differing degrees of inflammation that might be affected by genetic predisposition.
Keywords: Fibroproliferation; Hypertrophic scar; Inflammation; Keloid; Scar pathology.
© 2012 The Authors. International Wound Journal © 2012 Medicalhelplines.com Inc and John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Figures

References
-
- Bran GM, Goessler UR, Hormann K, Riedel F, Sadick H. Keloids: current concepts of pathogenesis (review). Int J Mol Med 2009;24: 283–93. - PubMed
-
- Aarabi S, Bhatt KA, Shi Y, Paterno J, Chang EI, Loh SA, Holmes JW, Longaker MT, Yee H, Gurtner GC. Mechanical load initiates hypertrophic scar formation through decreased cellular apoptosis. FASEB J 2007;21:3250–61. - PubMed
-
- Lee JY, Yang CC, Chao SC, Wong TW. Histopathological differential diagnosis of keloid and hypertrophic scar. Am J Dermatopathol 2004;26:379–84. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

