MirSNP, a database of polymorphisms altering miRNA target sites, identifies miRNA-related SNPs in GWAS SNPs and eQTLs
- PMID: 23173617
- PMCID: PMC3582533
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2164-13-661
MirSNP, a database of polymorphisms altering miRNA target sites, identifies miRNA-related SNPs in GWAS SNPs and eQTLs
Abstract
Background: Numerous single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) associated with complex diseases have been identified by genome-wide association studies (GWAS) and expression quantitative trait loci (eQTLs) studies. However, few of these SNPs have explicit biological functions. Recent studies indicated that the SNPs within the 3'UTR regions of susceptibility genes could affect complex traits/diseases by affecting the function of miRNAs. These 3'UTR SNPs are functional candidates and therefore of interest to GWAS and eQTL researchers.
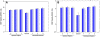
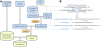
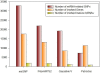
Description: We developed a publicly available online database, MirSNP (http://cmbi.bjmu.edu.cn/mirsnp), which is a collection of human SNPs in predicted miRNA-mRNA binding sites. We identified 414,510 SNPs that might affect miRNA-mRNA binding. Annotations were added to these SNPs to predict whether a SNP within the target site would decrease/break or enhance/create an miRNA-mRNA binding site. By applying MirSNP database to three brain eQTL data sets, we identified four unreported SNPs (rs3087822, rs13042, rs1058381, and rs1058398), which might affect miRNA binding and thus affect the expression of their host genes in the brain. We also applied the MirSNP database to our GWAS for schizophrenia: seven predicted miRNA-related SNPs (p < 0.0001) were found in the schizophrenia GWAS. Our findings identified the possible functions of these SNP loci, and provide the basis for subsequent functional research.
Conclusion: MirSNP could identify the putative miRNA-related SNPs from GWAS and eQTLs researches and provide the direction for subsequent functional researches.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Pinpointing miRNA and genes enrichment over trait-relevant tissue network in Genome-Wide Association Studies.BMC Med Genomics. 2020 Dec 28;13(Suppl 11):191. doi: 10.1186/s12920-020-00830-w. BMC Med Genomics. 2020. PMID: 33371893 Free PMC article.
-
SNPs at 3'UTR of APOL1 and miR-6741-3p target sites associated with kidney diseases more susceptible to SARS-COV-2 infection: in silco and in vitro studies.Mamm Genome. 2021 Oct;32(5):389-400. doi: 10.1007/s00335-021-09880-6. Epub 2021 Jun 4. Mamm Genome. 2021. PMID: 34089082 Free PMC article.
-
PolymiRTS Database 2.0: linking polymorphisms in microRNA target sites with human diseases and complex traits.Nucleic Acids Res. 2012 Jan;40(Database issue):D216-21. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkr1026. Epub 2011 Nov 10. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012. PMID: 22080514 Free PMC article.
-
Polymorphisms in Non-coding RNA Genes and Their Targets Sites as Risk Factors of Sporadic Colorectal Cancer.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2016;937:123-49. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-42059-2_7. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2016. PMID: 27573898 Review.
-
[Schizophrenia-associated single nucleotide polymorphisms affecting microRNA function].Yi Chuan. 2019 Aug 20;41(8):677-685. doi: 10.16288/j.yczz.19-126. Yi Chuan. 2019. PMID: 31447419 Review. Chinese.
Cited by
-
Candidate gene association studies: a comprehensive guide to useful in silico tools.BMC Genet. 2013 May 9;14:39. doi: 10.1186/1471-2156-14-39. BMC Genet. 2013. PMID: 23656885 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Rare genetic variant burden in DPYD predicts severe fluoropyrimidine-related toxicity risk.Biomed Pharmacother. 2022 Oct;154:113644. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2022.113644. Epub 2022 Sep 2. Biomed Pharmacother. 2022. PMID: 36063648 Free PMC article.
-
Rs6757 in microRNA-3976 binding site of CD147 confers risk of hepatocellular carcinoma in South Chinese population.World J Surg Oncol. 2022 Aug 17;20(1):260. doi: 10.1186/s12957-022-02724-w. World J Surg Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35978360 Free PMC article.
-
Computational analysis of functional single nucleotide polymorphisms associated with the CYP11B2 gene.PLoS One. 2014 Aug 7;9(8):e104311. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0104311. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 25102047 Free PMC article.
-
lncRNASNP: a database of SNPs in lncRNAs and their potential functions in human and mouse.Nucleic Acids Res. 2015 Jan;43(Database issue):D181-6. doi: 10.1093/nar/gku1000. Epub 2014 Oct 20. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015. PMID: 25332392 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Krol J, Loedige I, Filipowicz W. The widespread regulation of microRNA biogenesis, function and decay. Nat Rev Genet. 2010;11(9):597–610. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

