Sexual asthenia: Tradamixina versus Tadalafil 5 mg daily
- PMID: 23173697
- PMCID: PMC3499213
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2482-12-S1-S23
Sexual asthenia: Tradamixina versus Tadalafil 5 mg daily
Abstract
Background: Reduced libido is widely considered the most prominent symptomatic reflection of low testosterone (T) levels in men. Testosterone deficiency (TD) afflicts approximately 30% of men aged 40-79 years. This study seeks to evaluate the effect of a new natural compound "tradamixina "in order to improve male sexual function in elderly men, particularly libido and possible erectile dysfunction, versus administration of tadalafil 5 mg daily.
Methods: Seventy patients (67.3 ± 3.7 years) with stable marital relations and affected by reduced libido, with or without erectile dysfunction were recruited. They were randomly separated in 2 groups A-B of 35. Group A was administered twice a day a new compound "Tradamixina" (150 mg of Alga Ecklonia Bicyclis, 396 mg of Tribulus Terrestris and 144 mg of D-Glucosamine and N-Acetyl-D-Glucosamine) for two months, while Group B was administered tadalafil 5 mg daily, for two months. At visit and after 60 days of treatment patients were evaluated by means of detailed medical and sexual history, clinical examination, laboratory investigations (Total and Free T), instrumental examination (NPTR- nocturnal penile tumescence and rigidity test- with Rigiscan). Patients completed a self-administered IIEF questionnaire (The international index of erectile function) and SQoLM questionnaire (Sexual quality of life Questionnarie-Male). The results pre and post treatment were compared by Student t test (p<0.005).
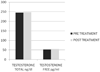
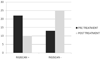
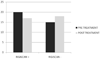
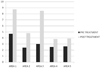
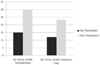
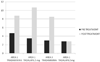
Results: After 2 months of treatment in group A serum TT levels (230 ± 18 ng/dl vs 671 ± 14 ng/dl ) and FT levels(56 ± 2.4 pg/ml vs 120 ± 3.9 pg/ml) increased, while in group B serum TT levels (245 ± 12 ng/dl vs 247 ± 15 ng/dl ) and FT levels(53 ± 0.3 pg/ml vs 55 ± 0.5 pg/ml) increased not statistically significant. The patient's numbers with negative NPTR improved after treatment in group A and B (15 vs 18 and 13 vs 25 respectively). The IIEF total score in group A increased after treatment with tradamixina (15 ± 1.5 vs 29.77 ± 1.2); the IIEF total score in group B increased slightly (12 ± 1.3 vs 23.40 ± 1.2). The SQoLM total score improved in both groups (A:16 ± 2,3 vs 33 ± 4,1 and B: 16 ± 3,4 vs 31 ± 2,1).
Conclusion: The treatment twice a day with "Tradamixina" for 2 months improved libido in elderly men without side effects of Tadalafil.
Figures


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

