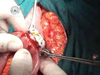
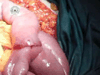
Sutureless jejuno-jejunal anastomosis in gastric cancer patients: a comparison with handsewn procedure in a single institute
- PMID: 23173807
- PMCID: PMC3499244
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2482-12-S1-S27
Sutureless jejuno-jejunal anastomosis in gastric cancer patients: a comparison with handsewn procedure in a single institute
Abstract
Background: The biofragmentable anastomotic ring has been used to this day for various types of anastomosis in the gastrointestinal tract, but it has not yet achieved widespread acceptance among surgeons. The purpose of this retrospective study is to compare surgical outcomes of sutureless with suture method of Roux-and-Y jejunojejunostomy in patients with gastric cancer.
Methods: Two groups of patients were obtained based on anastomosis technique (sutureless group versus hand sewn group): perioperative outcomes were recorded for every patient.
Results: The mean time spent to complete a sutureless anastomosis was 11 ± 4 min, whereas the time spent to perform hand sewn anastomosis was 23 ± 7 min. Estimated intraoperative blood loss was 178 ± 32 ml in the sutureless group and 182 ± 23 ml in the suture-method group with no significant differences. No complications were registered related to enteroanastomosis. Intraoperative mortality was none for both groups.
Conclusions: The Biofragmentable Anastomotic Ring offers a safe and time-saving method for the jejuno-jejunal anastomosis in gastric cancer surgery, and for this purpose the ring has been approved as a standard method in our clinic. Nevertheless currently there are few studies on upper gastrointestinal sutureless anastomoses and this could be the reason for the low uptake of this device.
Figures
References
-
- Amat C. Appareils a sutures: Les viroles de denans; les points de Bonnier: Les boutons de Murphy. Arch Med Pharmacie Militaires Paris. 1895;25:273–85.
-
- Murphy JB. Cholecysto-intestinal, gastro-intestinal, entero-intestinal anastomosis, and approximation without sutures. Med Rec N Y. 1892;42:665–76.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical