Targeting the Bcl-2 family for cancer therapy
- PMID: 23173842
- PMCID: PMC3955095
- DOI: 10.1517/14728222.2013.733001
Targeting the Bcl-2 family for cancer therapy
Abstract
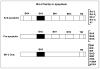
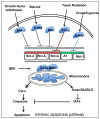
Introduction: Programmed cell death is well-orchestrated process regulated by multiple pro-apoptotic and anti-apoptotic genes, particularly those of the Bcl-2 gene family. These genes are well documented in cancer with aberrant expression being strongly associated with resistance to chemotherapy and radiation.
Areas covered: This review focuses on the resistance induced by the Bcl-2 family of anti-apoptotic proteins and current therapeutic interventions currently in preclinical or clinical trials that target this pathway. Major resistance mechanisms that are regulated by Bcl-2 family proteins and potential strategies to circumvent resistance are also examined. Although antisense and gene therapy strategies are used to nullify Bcl-2 family proteins, recent approaches use small molecule inhibitors (SMIs) and peptides. Structural similarity of the Bcl-2 family of proteins greatly favors development of inhibitors that target the BH3 domain, called BH3 mimetics.
Expert opinion: Strategies to specifically identify and inhibit critical determinants that promote therapy resistance and tumor progression represent viable approaches for developing effective cancer therapies. From a clinical perspective, pretreatment with novel, potent Bcl-2 inhibitors either alone or in combination with conventional therapies hold significant promise for providing beneficial clinical outcomes. Identifying SMIs with broader and higher affinities for inhibiting all of the Bcl-2 pro-survival proteins will facilitate development of superior cancer therapies.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Ellis HM, Horvitz HR. Genetic control of programmed cell death in the nematode C. elegans. Cell. 1986 Mar 28;44(6):817–29. - PubMed
-
- Bakshi A, Jensen JP, Goldman P, et al. Cloning the cromosomal break point of the t(14,18) human lymphomas, clustering around JH on chromosome 14 and near a transcriptional unit. Cell. 1985;41(18) First demonstration of significance of Bcl-2 family of proteins. - PubMed
-
- Cleary ML, Smith SD, Sklar J. Cloning and structural analysis of cDNAs for bcl-2 and a hybrid bcl-2/immunoglobulin transcript resulting from the t(14;18) translocation. Cell. 1986 Oct 10;47(1):19–28. - PubMed
-
- Tsujimoto Y, Cossman J, Jaffe E, Croce CM. Involvement of the bcl-2 gene in human follicular lymphoma. Science. 1985 Jun 21;228(4706):1440–3. - PubMed
-
- Vaux DL, Cory S, Adams JM. Bcl-2 gene promotes haemopoietic cell survival and cooperates with c-myc to immortalize pre-B cells. Nature. 1988 Sep 29;335(6189):440–2. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
