Evaluation of function predictions by PFP, ESG,and PSI-BLAST for moonlighting proteins
- PMID: 23173871
- PMCID: PMC3504920
- DOI: 10.1186/1753-6561-6-S7-S5
Evaluation of function predictions by PFP, ESG,and PSI-BLAST for moonlighting proteins
Abstract
Background: Advancements in function prediction algorithms are enabling large scale computational annotation for newly sequenced genomes. With the increase in the number of functionally well characterized proteins it has been observed that there are many proteins involved in more than one function. These proteins characterized as moonlighting proteins show varied functional behavior depending on the cell type, localization in the cell, oligomerization, multiple binding sites, etc. The functional diversity shown by moonlighting proteins may have significant impact on the traditional sequence based function prediction methods. Here we investigate how well diverse functions of moonlighting proteins can be predicted by some existing function prediction methods.
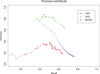
Results: We have analyzed the performances of three major sequence based function prediction methods,PSI-BLAST, the Protein Function Prediction (PFP), and the Extended Similarity Group (ESG) on predicting diverse functions of moonlighting proteins. In predicting discrete functions of a set of 19 experimentally identified moonlighting proteins, PFP showed overall highest recall among the three methods. Although ESG showed the highest precision, its recall was lower than PSI-BLAST. Recall by PSI-BLAST greatly improved when BLOSUM45 was used instead of BLOSUM62.
Conclusion: We have analyzed the performances of PFP, ESG, and PSI-BLAST in predicting the functional diversity of moonlighting proteins. PFP shows overall better performance in predicting diverse moonlighting functions as compared with PSI-BLAST and ESG. Recall by PSI-BLAST greatly improved when BLOSUM45 was used. This analysis indicates that considering weakly similar sequences in prediction enhances the performance of sequence based AFP methods in predicting functional diversity of moonlighting proteins. The current study will also motivate development of novel computational frameworks for automatic identification of such proteins.
Figures

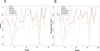
Similar articles
-
Computational characterization of moonlighting proteins.Biochem Soc Trans. 2014 Dec;42(6):1780-5. doi: 10.1042/BST20140214. Biochem Soc Trans. 2014. PMID: 25399606 Free PMC article. Review.
-
In-depth performance evaluation of PFP and ESG sequence-based function prediction methods in CAFA 2011 experiment.BMC Bioinformatics. 2013;14 Suppl 3(Suppl 3):S2. doi: 10.1186/1471-2105-14-S3-S2. Epub 2013 Feb 28. BMC Bioinformatics. 2013. PMID: 23514353 Free PMC article.
-
ESG: extended similarity group method for automated protein function prediction.Bioinformatics. 2009 Jul 15;25(14):1739-45. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btp309. Epub 2009 May 12. Bioinformatics. 2009. PMID: 19435743 Free PMC article.
-
The PFP and ESG protein function prediction methods in 2014: effect of database updates and ensemble approaches.Gigascience. 2015 Sep 14;4:43. doi: 10.1186/s13742-015-0083-4. eCollection 2015. Gigascience. 2015. PMID: 26380077 Free PMC article.
-
Can bioinformatics help in the identification of moonlighting proteins?Biochem Soc Trans. 2014 Dec;42(6):1692-7. doi: 10.1042/BST20140241. Biochem Soc Trans. 2014. PMID: 25399591 Review.
Cited by
-
Identification of Moonlighting Proteins in Genomes Using Text Mining Techniques.Proteomics. 2018 Nov;18(21-22):e1800083. doi: 10.1002/pmic.201800083. Epub 2018 Oct 10. Proteomics. 2018. PMID: 30260564 Free PMC article.
-
Role of Moonlighting Proteins in Disease: Analyzing the Contribution of Canonical and Moonlighting Functions in Disease Progression.Cells. 2023 Jan 5;12(2):235. doi: 10.3390/cells12020235. Cells. 2023. PMID: 36672169 Free PMC article.
-
De novo Prediction of Moonlighting Proteins Using Multimodal Deep Ensemble Learning.Front Genet. 2021 Mar 22;12:630379. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2021.630379. eCollection 2021. Front Genet. 2021. PMID: 33828582 Free PMC article.
-
Understanding protein multifunctionality: from short linear motifs to cellular functions.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2019 Nov;76(22):4407-4412. doi: 10.1007/s00018-019-03273-4. Epub 2019 Aug 20. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2019. PMID: 31432235 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Computational characterization of moonlighting proteins.Biochem Soc Trans. 2014 Dec;42(6):1780-5. doi: 10.1042/BST20140214. Biochem Soc Trans. 2014. PMID: 25399606 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

