Dose sparing and enhanced immunogenicity of inactivated rotavirus vaccine administered by skin vaccination using a microneedle patch
- PMID: 23174199
- PMCID: PMC4610374
- DOI: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2012.11.027
Dose sparing and enhanced immunogenicity of inactivated rotavirus vaccine administered by skin vaccination using a microneedle patch
Abstract
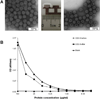
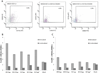
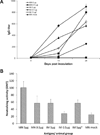
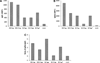
Skin immunization is effective against a number of infectious diseases, including smallpox and tuberculosis, but is difficult to administer. Here, we assessed the use of an easy-to-administer microneedle (MN) patch for skin vaccination using an inactivated rotavirus vaccine (IRV) in mice. Female inbred BALB/c mice in groups of six were immunized once in the skin using MN coated with 5 μg or 0.5 μg of inactivated rotavirus antigen or by intramuscular (IM) injection with 5 μg or 0.5 μg of the same antigen, bled at 0 and 10 days, and exsanguinated at 28 days. Rotavirus-specific IgG titers increased over time in sera of mice immunized with IRV using MN or IM injection. However, titers of IgG and neutralizing activity were generally higher in MN immunized mice than in IM immunized mice; the titers in mice that received 0.5 μg of antigen with MN were comparable or higher than those that received 5 μg of antigen IM, indicating dose sparing. None of the mice receiving negative-control, antigen-free MN had any IgG titers. In addition, MN immunization was at least as effective as IM administration in inducing a memory response of dendritic cells in the spleen. Our findings demonstrate that MN delivery can reduce the IRV dose needed to mount a robust immune response compared to IM injection and holds promise as a strategy for developing a safer and more effective rotavirus vaccine for use among children throughout the world.
Keywords: IRV; Microneedle; Rotavirus; Skin immunization.
Published by Elsevier Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Tate JE, Burton AH, Boschi-Pinto C, Steele AD, Duque J, Parashar UD, et al. 2008 estimate of worldwide rotavirus-associated mortality in children younger than 5 years before the introduction of universal rotavirus vaccination programmes: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Infect Dis. 2012;12:136–141. - PubMed
-
- Ruiz-Palacios GM, Perez-Schael I, Velazquez FR, Abate H, Breuer T, Clemens SC, et al. Safety and efficacy of an attenuated vaccine against severe rotavirus gastroenteritis. N Engl J Med. 2006;354:11–22. - PubMed
-
- Vesikari T, Matson DO, Dennehy P, Van Damme P, Santosham M, Rodriguez Z, et al. Safety and efficacy of a pentavalent human–bovine (WC3) reassortant rotavirus vaccine. N Engl J Med. 2006;354:23–33. [see comment] - PubMed
-
- Madhi SA, Cunliffe NA, Steele D, Witte D, Kirsten M, Louw C, et al. Effect of human rotavirus vaccine on severe diarrhea in African infants. N Engl J Med. 2010;362:289–298. - PubMed
-
- Zaman K, Dang DA, Victor JC, Shin S, Yunus M, Dallas MJ, et al. Efficacy of pentavalent rotavirus vaccine against severe rotavirus gastroenteritis in infants in developing countries in Asia: a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Lancet. 2010;376:615–623. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

