Cleavage of interferon regulatory factor 7 by enterovirus 71 3C suppresses cellular responses
- PMID: 23175366
- PMCID: PMC3554134
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.01855-12
Cleavage of interferon regulatory factor 7 by enterovirus 71 3C suppresses cellular responses
Abstract
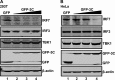
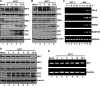
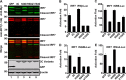
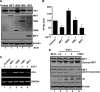
Enterovirus 71 (EV71) is a positive-stranded RNA virus which is capable of inhibiting innate immunity. Among virus-encoded proteins, the 3C protein compromises the type I interferon (IFN-I) response mediated by retinoid acid-inducible gene-I (RIG-I) or Toll-like receptor 3 that activates interferon regulatory 3 (IRF3) and IRF7. In the present study, we report that enterovirus 71 downregulates IRF7 through the 3C protein, which inhibits the function of IRF7. When expressed in mammalian cells, the 3C protein mediates cleavage of IRF7 rather than that of IRF3. This process is insensitive to inhibitors of caspase, proteasome, lysosome, and autophagy. H40D substitution in the 3C active site abolishes its activity, whereas R84Q or V154S substitution in the RNA binding motif has no effect. Furthermore, 3C-mediated cleavage occurs at the Q189-S190 junction within the constitutive activation domain of IRF7, resulting in two cleaved IRF7 fragments that are incapable of activating IFN expression. Ectopic expression of wild-type IRF7 limits EV71 replication. On the other hand, expression of the amino-terminal domain of IRF7 enhances EV71 infection, which correlates with its ability to interact with and inhibit IRF3. These results suggest that control of IRF7 by the 3C protein may represent a viral mechanism to escape cellular responses.
Figures






References
-
- McMinn PC. 2002. An overview of the evolution of enterovirus 71 and its clinical and public health significance. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 26:91–107 - PubMed
-
- Shih SR, Chiang C, Chen TC, Wu CN, Hsu JT, Lee JC, Hwang MJ, Li ML, Chen GW, Ho MS. 2004. Mutations at KFRDI and VGK domains of enterovirus 71 3C protease affect its RNA binding and proteolytic activities. J. Biomed. Sci. 11:239–248 - PubMed
-
- Sim AC, Luhur A, Tan TM, Chow VT, Poh CL. 2005. RNA interference against enterovirus 71 infection. Virology 341:72–79 - PubMed
-
- Li ML, Hsu TA, Chen TC, Chang SC, Lee JC, Chen CC, Stollar V, Shih SR. 2002. The 3C protease activity of enterovirus 71 induces human neural cell apoptosis. Virology 293:386–395 - PubMed
-
- Weng KF, Li ML, Huang CT, Shih SR. 2009. Enterovirus 71 3C protease cleaves a novel target CstF-64 and inhibits cellular polyadenylation. PLoS Pathog. 5:e1000593 doi:10.1371/journal.ppat.1000593 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

