Reactive oxygen species are induced by Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus early during primary infection of endothelial cells to promote virus entry
- PMID: 23175375
- PMCID: PMC3554172
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.02958-12
Reactive oxygen species are induced by Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus early during primary infection of endothelial cells to promote virus entry
Abstract
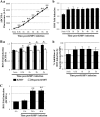
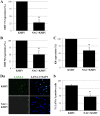
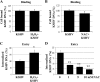
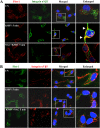
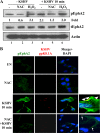
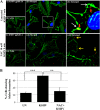
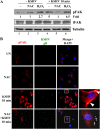
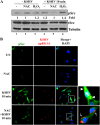
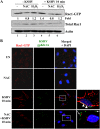
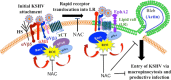
The entry of Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus (KSHV) into human dermal microvascular endothelial cells (HMVEC-d), natural in vivo target cells, via macropinocytosis is initiated through a multistep process involving the binding of KSHV envelope glycoproteins with cell surface α3β1, αVβ3, and αVβ5 integrin molecules and tyrosine kinase ephrin-A2 receptor, followed by the activation of preexisting integrin-associated signaling molecules such as focal adhesion kinase (FAK), Src, c-Cbl, phosphoinositide 3-kinase (PI-3K), and Rho-GTPases. Many viruses, including KSHV, utilize cellular reactive oxygen species (ROS) for viral genomic replication and survival within host cells; however, the role of ROS in early events of viral entry and the induction of signaling has not been elucidated. Here we show that KSHV induced ROS production very early during the infection of HMVEC-d cells and that ROS production was sustained over the observation period (24 h postinfection). ROS induction was dependent on the binding of KSHV to the target cells, since pretreatment of the virus with heparin abolished ROS induction. Pretreatment of HMVEC-d cells with the antioxidant N-acetylcysteine (NAC) significantly inhibited KSHV entry, and consequently gene expression, without affecting virus binding. In contrast, H(2)O(2) treatment increased the levels of KSHV entry and infection. In addition, NAC inhibited KSHV infection-induced translocation of αVβ3 integrin into lipid rafts, actin-dependent membrane perturbations, such as blebs, observed during macropinocytosis, and activation of the signal molecules ephrin-A2 receptor, FAK, Src, and Rac1. In contrast, H(2)O(2) treatment increased the activation of ephrin-A2, FAK, Src, and Rac1. These studies demonstrate that KSHV infection induces ROS very early during infection to amplify the signaling pathways necessary for its efficient entry into HMVEC-d cells via macropinocytosis.
Figures
Similar articles
-
CIB1 synergizes with EphrinA2 to regulate Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus macropinocytic entry in human microvascular dermal endothelial cells.PLoS Pathog. 2014 Feb 13;10(2):e1003941. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1003941. eCollection 2014 Feb. PLoS Pathog. 2014. PMID: 24550731 Free PMC article.
-
Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus interacts with EphrinA2 receptor to amplify signaling essential for productive infection.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012 May 8;109(19):E1163-72. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1119592109. Epub 2012 Apr 16. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012. PMID: 22509030 Free PMC article.
-
Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus forms a multimolecular complex of integrins (alphaVbeta5, alphaVbeta3, and alpha3beta1) and CD98-xCT during infection of human dermal microvascular endothelial cells, and CD98-xCT is essential for the postentry stage of infection.J Virol. 2008 Dec;82(24):12126-44. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01146-08. Epub 2008 Oct 1. J Virol. 2008. PMID: 18829766 Free PMC article.
-
KSHV Entry and Trafficking in Target Cells-Hijacking of Cell Signal Pathways, Actin and Membrane Dynamics.Viruses. 2016 Nov 14;8(11):305. doi: 10.3390/v8110305. Viruses. 2016. PMID: 27854239 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Insight into the Roles of E3 Ubiquitin Ligase c-Cbl, ESCRT Machinery, and Host Cell Signaling in Kaposi's Sarcoma-Associated Herpesvirus Entry and Trafficking.J Virol. 2018 Jan 30;92(4):e01376-17. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01376-17. Print 2018 Feb 15. J Virol. 2018. PMID: 29167336 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Human Herpesvirus 8 infection may contribute to oxidative stress in diabetes type 2 patients.BMC Res Notes. 2020 Feb 13;13(1):75. doi: 10.1186/s13104-020-4935-3. BMC Res Notes. 2020. PMID: 32054515 Free PMC article.
-
Synthetic antioxidants from a natural source can overtake the oncogenic stress management system and activate the stress‑sensitized death of KSHV‑infected cancer cells.Int J Mol Med. 2022 Sep;50(3):117. doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2022.5173. Epub 2022 Jul 20. Int J Mol Med. 2022. PMID: 35856421 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of total flavonoids of Spatholobus suberectus Dunn on PCV2 induced oxidative stress in RAW264.7 cells.BMC Complement Altern Med. 2017 May 2;17(1):244. doi: 10.1186/s12906-017-1764-6. BMC Complement Altern Med. 2017. PMID: 28464928 Free PMC article.
-
Modulation of host ROS metabolism is essential for viral infection of a bloom-forming coccolithophore in the ocean.ISME J. 2016 Jul;10(7):1742-54. doi: 10.1038/ismej.2015.228. Epub 2016 Jan 19. ISME J. 2016. PMID: 26784355 Free PMC article.
-
Extracellular vesicles from KSHV-infected endothelial cells activate the complement system.Oncotarget. 2017 Oct 9;8(59):99841-99860. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.21668. eCollection 2017 Nov 21. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 29245944 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Cesarman E, Chang Y, Moore PS, Said JW, Knowles DM. 1995. Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus-like DNA sequences in AIDS-related body-cavity-based lymphomas. N. Engl. J. Med. 332:1186–1191 - PubMed
-
- Ganem D. 2007. Kaposi‘s sarcoma-associated herpesvirus, p 2847–2888 In Knipe DM, Howley PM, Griffin DE, Lamb RA, Martin MA, Roizman B, Straus SE. (ed), Fields virology, 5th ed, vol 2 Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Philadelphia, PA
-
- Krishnan HH, Naranatt PP, Smith MS, Zeng L, Bloomer C, Chandran B. 2004. Concurrent expression of latent and a limited number of lytic genes with immune modulation and antiapoptotic function by Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus early during infection of primary endothelial and fibroblast cells and subsequent decline of lytic gene expression. J. Virol. 78:3601–3620 - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

