Default-mode network disruption in mild traumatic brain injury
- PMID: 23175546
- PMCID: PMC3504316
- DOI: 10.1148/radiol.12120748
Default-mode network disruption in mild traumatic brain injury
Abstract
Purpose: To investigate the integrity of the default-mode network (DMN) by using independent component analysis (ICA) methods in patients shortly after mild traumatic brain injury (MTBI) and healthy control subjects, and to correlate DMN connectivity changes with neurocognitive tests and clinical symptoms.
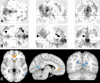
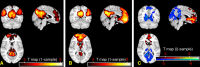
Materials and methods: This study was approved by the institutional review board and complied with HIPAA regulations. Twenty-three patients with MTBI who had posttraumatic symptoms shortly after injury (<2 months) and 18 age-matched healthy control subjects were included in this study. Resting-state functional magnetic resonance imaging was performed at 3 T to characterize the DMN by using ICA methods, including a single-participant ICA on the basis of a comprehensive template from core seeds in the posterior cingulate cortex (PCC) and medial prefrontal cortex (MPFC) nodes. ICA z images of DMN components were compared between the two groups and correlated with neurocognitive tests and clinical performance in patients by using Pearson and Spearman rank correlation.
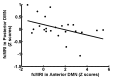
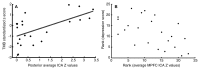
Results: When compared with the control subjects, there was significantly reduced connectivity in the PCC and parietal regions and increased frontal connectivity around the MPFC in patients with MTBI (P < .01). These frontoposterior opposing changes within the DMN were significantly correlated (r = -0.44, P = .03). The reduced posterior connectivity correlated positively with neurocognitive dysfunction (eg, cognitive flexibility), while the increased frontal connectivity correlated negatively with posttraumatic symptoms (ie, depression, anxiety, fatigue, and postconcussion syndrome).
Conclusion: These results showed abnormal DMN connectivity patterns in patients with MTBI, which may provide insight into how neuronal communication and information integration are disrupted among DMN key structures after mild head injury.
© RSNA, 2012.
Figures

References
-
- Sosin DM, Sniezek JE, Thurman DJ. Incidence of mild and moderate brain injury in the United States, 1991. Brain Inj 1996;10(1):47–54 - PubMed
-
- Cassidy JD, Carroll LJ, Peloso PM, et al. Incidence, risk factors and prevention of mild traumatic brain injury: results of the WHO Collaborating Centre Task Force on Mild Traumatic Brain Injury. J Rehabil Med 2004;(43 Suppl):28–60 - PubMed
-
- Carroll LJ, Cassidy JD, Peloso PM, et al. Prognosis for mild traumatic brain injury: results of the WHO Collaborating Centre Task Force on Mild Traumatic Brain Injury. J Rehabil Med 2004;(43 Suppl):84–105 - PubMed
-
- Rutland-Brown W, Langlois JA, Thomas KE, Xi YL. Incidence of traumatic brain injury in the United States, 2003. J Head Trauma Rehabil 2006;21(6):544–548 - PubMed
-
- Silver JM, McAllister TW, Yudofsky SC. Textbook of traumatic brain injury. 2nd ed. Washington, DC: American Psychiatric Publishing, 2011
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

