Position-dependent splicing activation and repression by SR and hnRNP proteins rely on common mechanisms
- PMID: 23175589
- PMCID: PMC3527730
- DOI: 10.1261/rna.037044.112
Position-dependent splicing activation and repression by SR and hnRNP proteins rely on common mechanisms
Erratum in
- RNA. 2013 Jul;19(7):1015
Abstract
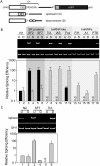
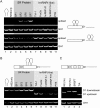
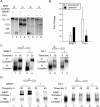
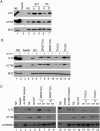
Alternative splicing is regulated by splicing factors that modulate splice site selection. In some cases, however, splicing factors show antagonistic activities by either activating or repressing splicing. Here, we show that these opposing outcomes are based on their binding location relative to regulated 5' splice sites. SR proteins enhance splicing only when they are recruited to the exon. However, they interfere with splicing by simply relocating them to the opposite intronic side of the splice site. hnRNP splicing factors display analogous opposing activities, but in a reversed position dependence. Activation by SR or hnRNP proteins increases splice site recognition at the earliest steps of exon definition, whereas splicing repression promotes the assembly of nonproductive complexes that arrest spliceosome assembly prior to splice site pairing. Thus, SR and hnRNP splicing factors exploit similar mechanisms to positively or negatively influence splice site selection.
Figures
Similar articles
-
An intron element modulating 5' splice site selection in the hnRNP A1 pre-mRNA interacts with hnRNP A1.Mol Cell Biol. 1997 Apr;17(4):1776-86. doi: 10.1128/MCB.17.4.1776. Mol Cell Biol. 1997. PMID: 9121425 Free PMC article.
-
HnRNP L-mediated regulation of mammalian alternative splicing by interference with splice site recognition.RNA Biol. 2010 Jan-Feb;7(1):56-64. doi: 10.4161/rna.7.1.10402. Epub 2010 Jan 21. RNA Biol. 2010. PMID: 19946215
-
Heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein G regulates splice site selection by binding to CC(A/C)-rich regions in pre-mRNA.J Biol Chem. 2009 May 22;284(21):14303-15. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M901026200. Epub 2009 Mar 12. J Biol Chem. 2009. PMID: 19282290 Free PMC article.
-
Splicing factors of SR and hnRNP families as regulators of apoptosis in cancer.Cancer Lett. 2017 Jun 28;396:53-65. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2017.03.013. Epub 2017 Mar 14. Cancer Lett. 2017. PMID: 28315432 Review.
-
hnRNP proteins and splicing control.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2007;623:123-47. doi: 10.1007/978-0-387-77374-2_8. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2007. PMID: 18380344 Review.
Cited by
-
Regulation of CD44E by DARPP-32-dependent activation of SRp20 splicing factor in gastric tumorigenesis.Oncogene. 2016 Apr 7;35(14):1847-56. doi: 10.1038/onc.2015.250. Epub 2015 Jun 29. Oncogene. 2016. PMID: 26119931 Free PMC article.
-
Differential alternative splicing genes and isoform co-expression networks of Brassica napus under multiple abiotic stresses.Front Plant Sci. 2022 Oct 13;13:1009998. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2022.1009998. eCollection 2022. Front Plant Sci. 2022. PMID: 36311064 Free PMC article.
-
Interpretation of mRNA splicing mutations in genetic disease: review of the literature and guidelines for information-theoretical analysis.F1000Res. 2014 Nov 18;3:282. doi: 10.12688/f1000research.5654.1. eCollection 2014. F1000Res. 2014. PMID: 25717368 Free PMC article. Review.
-
TNFα Mediates Inflammation-Induced Effects on PPARG Splicing in Adipose Tissue and Mesenchymal Precursor Cells.Cells. 2021 Dec 24;11(1):42. doi: 10.3390/cells11010042. Cells. 2021. PMID: 35011604 Free PMC article.
-
Combinatorial regulation of alternative splicing.Biochim Biophys Acta Gene Regul Mech. 2019 Nov-Dec;1862(11-12):194392. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagrm.2019.06.003. Epub 2019 Jul 2. Biochim Biophys Acta Gene Regul Mech. 2019. PMID: 31276857 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
