Levodopa-induced dyskinesia is strongly associated with resonant cortical oscillations
- PMID: 23175810
- PMCID: PMC6621755
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3047-12.2012
Levodopa-induced dyskinesia is strongly associated with resonant cortical oscillations
Abstract
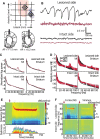
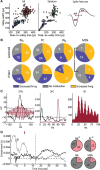
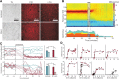
The standard pharmacological treatment for Parkinson's disease using the dopamine precursor levodopa is unfortunately limited by gradual development of disabling involuntary movements for which the underlying causes are poorly understood. Here we show that levodopa-induced dyskinesia in hemiparkinsonian rats is strongly associated with pronounced 80 Hz local field potential oscillations in the primary motor cortex following levodopa treatment. When this oscillation is interrupted by application of a dopamine antagonist onto the cortical surface the dyskinetic symptoms disappear. The finding that abnormal cortical oscillations are a key pathophysiological mechanism calls for a revision of the prevailing hypothesis that links levodopa-induced dyskinesia to an altered sensitivity to dopamine only in the striatum. Apart from having important implications for the treatment of Parkinson's disease, the discovered pathophysiological mechanism may also play a role in several other psychiatric and neurological conditions involving cortical dysfunction.
Figures

Similar articles
-
L-DOPA treatment selectively restores spine density in dopamine receptor D2-expressing projection neurons in dyskinetic mice.Biol Psychiatry. 2014 May 1;75(9):711-22. doi: 10.1016/j.biopsych.2013.05.006. Epub 2013 Jun 13. Biol Psychiatry. 2014. PMID: 23769604
-
The involvement of RGS9 in l-3,4-dihydroxyphenylalanine-induced dyskinesias in unilateral 6-OHDA lesion rat model.Brain Res Bull. 2011 Nov 25;86(5-6):367-72. doi: 10.1016/j.brainresbull.2011.09.016. Epub 2011 Sep 24. Brain Res Bull. 2011. PMID: 21963945
-
Controlled-release levodopa methyl ester/benserazide-loaded nanoparticles ameliorate levodopa-induced dyskinesia in rats.Int J Nanomedicine. 2012;7:2077-86. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S30463. Epub 2012 Apr 19. Int J Nanomedicine. 2012. PMID: 22619544 Free PMC article.
-
Pathogenesis of levodopa-induced dyskinesia: focus on D1 and D3 dopamine receptors.Parkinsonism Relat Disord. 2005 Jun;11 Suppl 1:S25-9. doi: 10.1016/j.parkreldis.2004.11.005. Parkinsonism Relat Disord. 2005. PMID: 15885624 Review.
-
Mechanisms underlying cortical resonant states: implications for levodopa-induced dyskinesia.Rev Neurosci. 2013;24(4):415-29. doi: 10.1515/revneuro-2013-0018. Rev Neurosci. 2013. PMID: 23907419 Review.
Cited by
-
Cerebellar stimulation prevents Levodopa-induced dyskinesia in mice and normalizes activity in a motor network.Nat Commun. 2022 Jun 9;13(1):3211. doi: 10.1038/s41467-022-30844-0. Nat Commun. 2022. PMID: 35680891 Free PMC article.
-
Alterations in primary motor cortex neurotransmission and gene expression in hemi-parkinsonian rats with drug-induced dyskinesia.Neuroscience. 2015 Dec 3;310:12-26. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2015.09.018. Epub 2015 Sep 9. Neuroscience. 2015. PMID: 26363150 Free PMC article.
-
Personalized chronic adaptive deep brain stimulation outperforms conventional stimulation in Parkinson's disease.medRxiv [Preprint]. 2023 Aug 8:2023.08.03.23293450. doi: 10.1101/2023.08.03.23293450. medRxiv. 2023. Update in: Nat Med. 2024 Nov;30(11):3345-3356. doi: 10.1038/s41591-024-03196-z. PMID: 37649907 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
Decoupling of motor cortex to movement in Parkinson's dyskinesia rescued by sub-anaesthetic ketamine.Brain. 2025 Jun 3;148(6):2135-2150. doi: 10.1093/brain/awae386. Brain. 2025. PMID: 39585797 Free PMC article.
-
Gamma Oscillations in the Hyperkinetic State Detected with Chronic Human Brain Recordings in Parkinson's Disease.J Neurosci. 2016 Jun 15;36(24):6445-58. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1128-16.2016. J Neurosci. 2016. PMID: 27307233 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alonso-Frech F, Zamarbide I, Alegre M, Rodríguez-Oroz MC, Guridi J, Manrique M, Valencia M, Artieda J, Obeso JA. Slow oscillatory activity and levodopa-induced dyskinesias in Parkinson's disease. Brain. 2006;129:1748–1757. - PubMed
-
- Aubert I, Guigoni C, Håkansson K, Li Q, Dovero S, Barthe N, Bioulac BH, Gross CE, Fisone G, Bloch B, Bezard E. Increased D1 dopamine receptor signaling in levodopa-induced dyskinesia. Ann Neurol. 2005;57:17–26. - PubMed
-
- Barthó P, Hirase H, Monconduit L, Zugaro M, Harris KD, Buzsáki G. Characterization of neocortical principal cells and interneurons by network interactions and extracellular features. J Neurophysiol. 2004;92:600–608. - PubMed
-
- Berke JD, Okatan M, Skurski J, Eichenbaum HB. Oscillatory entrainment of striatal neurons in freely moving rats. Neuron. 2004;43:883–896. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
