Contribution of cholinergic and GABAergic mechanisms to direction tuning, discriminability, response reliability, and neuronal rate correlations in macaque middle temporal area
- PMID: 23175816
- PMCID: PMC6621794
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0554-12.2012
Contribution of cholinergic and GABAergic mechanisms to direction tuning, discriminability, response reliability, and neuronal rate correlations in macaque middle temporal area
Abstract
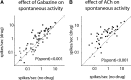
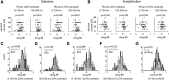
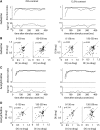
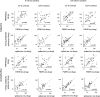
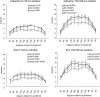
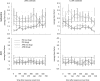
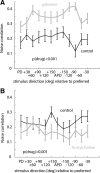
Previous studies have investigated the effects of acetylcholine (ACh) on neuronal tuning, coding, and attention in primary visual cortex, but its contribution to coding in extrastriate cortex is unexplored. Here we investigate the effects of ACh on tuning properties of macaque middle temporal area MT neurons and contrast them with effects of gabazine, a GABA(A) receptor blocker. ACh increased neuronal activity, it had no effect on tuning width, but it significantly increased the direction discriminability of a neuron. Gabazine equally increased neuronal activity, but it widened tuning curves and decreased the direction discriminability of a neuron. Although gabazine significantly reduced response reliability, ACh application had little effect on response reliability. Finally, gabazine increased noise correlation of simultaneously recorded neurons, whereas ACh reduced it. Thus, both drugs increased firing rates, but only ACh application improved neuronal tuning and coding in line with effects seen in studies in which attention was selectively manipulated.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Multiple types of GABAA receptors mediate inhibition in brain stem parasympathetic cardiac neurons in the nucleus ambiguus.J Neurophysiol. 2006 Dec;96(6):3266-72. doi: 10.1152/jn.00590.2006. Epub 2006 Aug 16. J Neurophysiol. 2006. PMID: 16914614
-
GABAergic and cholinergic modulation of repetition suppression in inferior temporal cortex.Sci Rep. 2018 Sep 3;8(1):13160. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-31515-1. Sci Rep. 2018. PMID: 30177749 Free PMC article.
-
Distributed and Dynamic Neural Encoding of Multiple Motion Directions of Transparently Moving Stimuli in Cortical Area MT.J Neurosci. 2015 Dec 9;35(49):16180-98. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2175-15.2015. J Neurosci. 2015. PMID: 26658869 Free PMC article.
-
Cholinergic suppression of visual responses in primate V1 is mediated by GABAergic inhibition.J Neurophysiol. 2012 Oct;108(7):1907-23. doi: 10.1152/jn.00188.2012. Epub 2012 Jul 11. J Neurophysiol. 2012. PMID: 22786955 Free PMC article.
-
A simple linear readout of MT supports motion direction-discrimination performance.J Neurophysiol. 2020 Feb 1;123(2):682-694. doi: 10.1152/jn.00117.2019. Epub 2019 Dec 18. J Neurophysiol. 2020. PMID: 31852399 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Illuminating the role of cholinergic signaling in circuits of attention and emotionally salient behaviors.Front Synaptic Neurosci. 2014 Oct 27;6:24. doi: 10.3389/fnsyn.2014.00024. eCollection 2014. Front Synaptic Neurosci. 2014. PMID: 25386136 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Monitoring the Right Collection: The Central Cholinergic Neurons as an Instructive Example.Front Neural Circuits. 2017 Apr 27;11:31. doi: 10.3389/fncir.2017.00031. eCollection 2017. Front Neural Circuits. 2017. PMID: 28496401 Free PMC article.
-
Cell class-specific modulation of attentional signals by acetylcholine in macaque frontal eye field.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2019 Oct 1;116(40):20180-20189. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1905413116. Epub 2019 Sep 16. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2019. PMID: 31527242 Free PMC article.
-
Cellular, Synaptic and Network Effects of Acetylcholine in the Neocortex.Front Neural Circuits. 2019 Apr 12;13:24. doi: 10.3389/fncir.2019.00024. eCollection 2019. Front Neural Circuits. 2019. PMID: 31031601 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Basal Forebrain Cholinergic Circuits and Signaling in Cognition and Cognitive Decline.Neuron. 2016 Sep 21;91(6):1199-1218. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2016.09.006. Neuron. 2016. PMID: 27657448 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Albright TD. Direction and orientation selectivity of neurons in visual area MT of the macaque. J Neurophysiol. 1984;52:1106–1130. - PubMed
-
- Anthony BL, Dennison RL, Aronstam RS. Disruption of muscarinic receptor-G protein coupling is a general property of liquid volatile anesthetics. Neurosci Lett. 1989;99:191–196. - PubMed
-
- Benjamini Y, Hochberg Y. Controlling the false discovery rate: a practical and powerful approach to multiple testing. J R Stat Soc Ser B Stat Methodol. 1995;57:289–300.
-
- Bisley JW, Zaksas D, Droll JA, Pasternak T. Activity of neurons in cortical area MT during a memory for motion task. J Neurophysiol. 2004;91:286–300. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
