Tumor-suppressive microRNA-135a inhibits cancer cell proliferation by targeting the c-MYC oncogene in renal cell carcinoma
- PMID: 23176581
- PMCID: PMC7657112
- DOI: 10.1111/cas.12072
Tumor-suppressive microRNA-135a inhibits cancer cell proliferation by targeting the c-MYC oncogene in renal cell carcinoma
Abstract
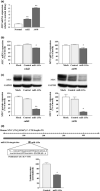
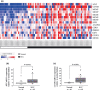
Recently, many studies have suggested that microRNAs (miRNAs) are involved in cancer cell development, invasion, and metastasis of various types of human cancers. In a previous study, miRNA expression signatures from renal cell carcinoma (RCC) revealed that expression of microRNA-135a (miR-135a) was significantly reduced in cancerous tissues. The aim of this study was to investigate the functional significance of miR-135a and to identify miR-135a-mediated molecular pathways in RCC cells. Restoration of mature miR-135a significantly inhibited cancer cell proliferation and induced G0 /G1 arrest in the RCC cell lines caki2 and A498, suggesting that miR-135a functioned as a potential tumor suppressor. We then examined miR-135a-mediated molecular pathways using genome-wide gene expression analysis and in silico analysis. A total of 570 downregulated genes were identified in miR-135a transfected RCC cell lines. To investigate the biological significance of potential miR-135a-mediated pathways, we classified putative miR-135a-regulated genes according to the Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomics pathway database. From our in silico analysis, 25 pathways, including the cell cycle, pathways in cancer, DNA replication, and focal adhesion, were significantly regulated by miR-135a in RCC cells. Moreover, based on the results of this analysis, we investigated whether miR-135a targeted the c-MYC gene in RCC. Gain-of-function and luciferase reporter assays showed that c-MYC was directly regulated by miR-135a in RCC cells. Furthermore, c-MYC expression was significantly upregulated in RCC clinical specimens. Our data suggest that elucidation of tumor-suppressive miR-135a-mediated molecular pathways could reveal potential therapeutic targets in RCC.
© 2012 Japanese Cancer Association.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Tumor-suppressive microRNA-1291 directly regulates glucose transporter 1 in renal cell carcinoma.Cancer Sci. 2013 Nov;104(11):1411-9. doi: 10.1111/cas.12240. Epub 2013 Aug 22. Cancer Sci. 2013. PMID: 23889809 Free PMC article.
-
Tumor suppressive microRNA-1285 regulates novel molecular targets: aberrant expression and functional significance in renal cell carcinoma.Oncotarget. 2012 Jan;3(1):44-57. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.417. Oncotarget. 2012. PMID: 22294552 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNA-218 inhibits cell migration and invasion in renal cell carcinoma through targeting caveolin-2 involved in focal adhesion pathway.J Urol. 2013 Sep;190(3):1059-68. doi: 10.1016/j.juro.2013.02.089. Epub 2013 Feb 27. J Urol. 2013. PMID: 23454155
-
MiR-135a biogenesis and regulation in malignancy: a new hope for cancer research and therapy.Cancer Biol Med. 2020 Aug 15;17(3):569-582. doi: 10.20892/j.issn.2095-3941.2020.0033. Cancer Biol Med. 2020. PMID: 32944391 Free PMC article. Review.
-
miRNAs as potential game-changers in renal cell carcinoma: Future clinical and medicinal uses.Pathol Res Pract. 2023 May;245:154439. doi: 10.1016/j.prp.2023.154439. Epub 2023 Apr 5. Pathol Res Pract. 2023. PMID: 37028108 Review.
Cited by
-
miR-135a Inhibits the Invasion and Migration of Esophageal Cancer Stem Cells through the Hedgehog Signaling Pathway by Targeting Smo.Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2020 Mar 6;19:841-852. doi: 10.1016/j.omtn.2019.10.037. Epub 2019 Nov 13. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2020. Retraction in: Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2021 Nov 17;26:1198. doi: 10.1016/j.omtn.2021.09.012. PMID: 31981861 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
Prognostic value of meta-signature miRNAs in renal cell carcinoma: an integrated miRNA expression profiling analysis.Sci Rep. 2015 May 14;5:10272. doi: 10.1038/srep10272. Sci Rep. 2015. PMID: 25974855 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNA-135a is involved in podocyte injury in a transient receptor potential channel 1-dependent manner.Int J Mol Med. 2017 Nov;40(5):1511-1519. doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2017.3152. Epub 2017 Sep 25. Int J Mol Med. 2017. PMID: 28949388 Free PMC article.
-
microRNA-99a-5p induces cellular senescence in gemcitabine-resistant bladder cancer by targeting SMARCD1.Mol Oncol. 2022 Mar;16(6):1329-1346. doi: 10.1002/1878-0261.13192. Epub 2022 Feb 28. Mol Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35148461 Free PMC article.
-
An investigation into anti-proliferative effects of microRNAs encoded by the miR-106a-363 cluster on human carcinoma cells and keratinocytes using microarray profiling of miRNA transcriptomes.Front Genet. 2014 Aug 25;5:246. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2014.00246. eCollection 2014. Front Genet. 2014. PMID: 25202322 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Weng L, Wu X, Gao H et al MicorRNA profiling of clear cell renal carcinoma by whole‐genome small RNA deep sequencing of paired frozen and formalin‐fixed, paraffin‐embedded tissue specimens. J Pathol 2010; 222: 41–51. - PubMed
-
- Aben KK, Luth TK, Jassen‐Heijinen ML, Mulders PF, Kiemeney LA, van Spronsen DJ. No improvement in renal cell carcinoma survival: a population‐based study in The Netherlands. Eur J Cancer 2008; 44: 1701–9. - PubMed
-
- Filipowicz W, Bhattacharyya SN, Sonenberg N. Mechanism of post transcriptional regulation by microRNAs: are the answers in sight? Nat Rev Genet 2008; 9: 102–14. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

