Early life opportunities for prevention of diabetes in low and middle income countries
- PMID: 23176627
- PMCID: PMC3526388
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2458-12-1025
Early life opportunities for prevention of diabetes in low and middle income countries
Abstract
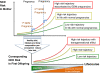
Background: The global burden of diabetes and other non-communicable diseases is rising dramatically worldwide and is causing a double poor health burden in low- and middle-income countries. Early life influences play an important part in this scenario because maternal lifestyle and conditions such as gestational diabetes and obesity affect the risk of diabetes in the next generation. This indicates important periods during the lifecourse when interventions could have powerful affects in reducing incidence of non-communicable diseases. However, interventions to promote diet and lifestyle in prospective parents before conception have not received sufficient attention, especially in low- and middle-income countries undergoing socio-economic transition.
Discussion: Interventions to produce weight loss in adults or to reduce weight gain in pregnancy have had limited success and might be too late to produce the largest effects on the health of the child and his/her later risk of non-communicable diseases. A very important factor in the prevention of the developmental component of diabetes risk is the physiological state in which the parents enter pregnancy. We argue that the most promising strategy to improve prospective parents' body composition and lifestyle is the promotion of health literacy in adolescents. Multiple but integrated forms of community-based interventions that focus on nutrition, physical activity, family planning, breastfeeding and infant feeding practices are needed. They need to address the wider social economic context in which adolescents live and to be linked with existing public health programmes in sexual and reproductive health and maternal and child health initiatives.
Summary: Interventions aimed at ensuring a healthy body composition, diet and lifestyle before pregnancy offer a most effective solution in many settings, especially in low- and middle-income countries undergoing socio-economic transition. Preparing a mother, her partner and her future child for "the 1000 days", whether from planned or unplanned conception would break the cycle of risk and demonstrate benefit in the shortest possible time. Such interventions will be particularly important in adolescents and young women in disadvantaged groups and can improve the physiological status of the fetus as well as reduce the prevalence of pregnancy conditions such as gestational diabetes mellitus which both predispose to non-communicables diseases in both the mother and her child. Pre-conception interventions require equipping prospective parents with the necessary knowledge and skills to make healthy lifestyle choices for themselves and their children. Addressing the promotion of such health literacy in parents-to-be in low- and middle-income countries requires a wider social perspective. It requires a range of multisectoral agencies to work together and could be linked to the issues of women's empowerment, to reproductive health, to communicable disease prevention and to the Millennium Development Goals 4 and 5.
Figures
References
-
- Diabetes Atlas. http://www.idf.org/diabetesatlas/5e/undiagnosed-diabetes]
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical