Alteration of fatty-acid-metabolizing enzymes affects mitochondrial form and function in hereditary spastic paraplegia
- PMID: 23176821
- PMCID: PMC3516610
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ajhg.2012.11.001
Alteration of fatty-acid-metabolizing enzymes affects mitochondrial form and function in hereditary spastic paraplegia
Abstract
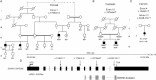
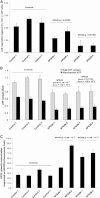
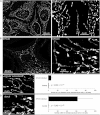
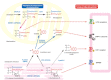
Hereditary spastic paraplegia (HSP) is considered one of the most heterogeneous groups of neurological disorders, both clinically and genetically. The disease comprises pure and complex forms that clinically include slowly progressive lower-limb spasticity resulting from degeneration of the corticospinal tract. At least 48 loci accounting for these diseases have been mapped to date, and mutations have been identified in 22 genes, most of which play a role in intracellular trafficking. Here, we identified mutations in two functionally related genes (DDHD1 and CYP2U1) in individuals with autosomal-recessive forms of HSP by using either the classical positional cloning or a combination of whole-genome linkage mapping and next-generation sequencing. Interestingly, three subjects with CYP2U1 mutations presented with a thin corpus callosum, white-matter abnormalities, and/or calcification of the basal ganglia. These genes code for two enzymes involved in fatty-acid metabolism, and we have demonstrated in human cells that the HSP pathophysiology includes alteration of mitochondrial architecture and bioenergetics with increased oxidative stress. Our combined results focus attention on lipid metabolism as a critical HSP pathway with a deleterious impact on mitochondrial bioenergetic function.
Copyright © 2012 The American Society of Human Genetics. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- Harding A.E. Classification of the hereditary ataxias and paraplegias. Lancet. 1983;1:1151–1155. - PubMed
-
- Tallaksen C.M., Dürr A., Brice A. Recent advances in hereditary spastic paraplegia. Curr. Opin. Neurol. 2001;14:457–463. - PubMed
-
- Fink J.K. Advances in the hereditary spastic paraplegias. Exp. Neurol. 2003;184(Suppl 1):S106–S110. - PubMed
-
- Schüle R., Schöls L. Genetics of hereditary spastic paraplegias. Semin. Neurol. 2011;31:484–493. - PubMed
-
- Finsterer J., Löscher W., Quasthoff S., Wanschitz J., Auer-Grumbach M., Stevanin G. Hereditary spastic paraplegias with autosomal dominant, recessive, X-linked, or maternal trait of inheritance. J. Neurol. Sci. 2012;318:1–18. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

