Mutations in DDHD2, encoding an intracellular phospholipase A(1), cause a recessive form of complex hereditary spastic paraplegia
- PMID: 23176823
- PMCID: PMC3516595
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ajhg.2012.10.017
Mutations in DDHD2, encoding an intracellular phospholipase A(1), cause a recessive form of complex hereditary spastic paraplegia
Abstract
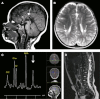
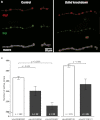
We report on four families affected by a clinical presentation of complex hereditary spastic paraplegia (HSP) due to recessive mutations in DDHD2, encoding one of the three mammalian intracellular phospholipases A(1) (iPLA(1)). The core phenotype of this HSP syndrome consists of very early-onset (<2 years) spastic paraplegia, intellectual disability, and a specific pattern of brain abnormalities on cerebral imaging. An essential role for DDHD2 in the human CNS, and perhaps more specifically in synaptic functioning, is supported by a reduced number of active zones at synaptic terminals in Ddhd-knockdown Drosophila models. All identified mutations affect the protein's DDHD domain, which is vital for its phospholipase activity. In line with the function of DDHD2 in lipid metabolism and its role in the CNS, an abnormal lipid peak indicating accumulation of lipids was detected with cerebral magnetic resonance spectroscopy, which provides an applicable diagnostic biomarker that can distinguish the DDHD2 phenotype from other complex HSP phenotypes. We show that mutations in DDHD2 cause a specific complex HSP subtype (SPG54), thereby linking a member of the PLA(1) family to human neurologic disease.
Copyright © 2012 The American Society of Human Genetics. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Mutations in phospholipase DDHD2 cause autosomal recessive hereditary spastic paraplegia (SPG54).Eur J Hum Genet. 2013 Nov;21(11):1214-8. doi: 10.1038/ejhg.2013.29. Epub 2013 Mar 13. Eur J Hum Genet. 2013. PMID: 23486545 Free PMC article.
-
Mutations in CYP2U1, DDHD2 and GBA2 genes are rare causes of complicated forms of hereditary spastic paraparesis.J Neurol. 2014 Feb;261(2):373-81. doi: 10.1007/s00415-013-7206-6. Epub 2013 Dec 13. J Neurol. 2014. PMID: 24337409
-
Defining the clinical-genetic and neuroradiological features in SPG54: description of eight additional cases and nine novel DDHD2 variants.J Neurol. 2019 Nov;266(11):2657-2664. doi: 10.1007/s00415-019-09466-y. Epub 2019 Jul 13. J Neurol. 2019. PMID: 31302745
-
Biallelic DDHD2 mutations in patients with adult-onset complex hereditary spastic paraplegia.Ann Clin Transl Neurol. 2023 Sep;10(9):1603-1612. doi: 10.1002/acn3.51850. Epub 2023 Jul 7. Ann Clin Transl Neurol. 2023. PMID: 37420318 Free PMC article.
-
Hereditary spastic paraplegia: advances in genetic research. Hereditary Spastic Paraplegia Working group.Neurology. 1996 Jun;46(6):1507-14. doi: 10.1212/wnl.46.6.1507. Neurology. 1996. PMID: 8649538 Review.
Cited by
-
Lipid Droplets in the Pathogenesis of Hereditary Spastic Paraplegia.Front Mol Biosci. 2021 May 10;8:673977. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2021.673977. eCollection 2021. Front Mol Biosci. 2021. PMID: 34041268 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Liver X receptor-agonist treatment rescues degeneration in a Drosophila model of hereditary spastic paraplegia.Acta Neuropathol Commun. 2022 Mar 28;10(1):40. doi: 10.1186/s40478-022-01343-6. Acta Neuropathol Commun. 2022. PMID: 35346366 Free PMC article.
-
Insights into Clinical, Genetic, and Pathological Aspects of Hereditary Spastic Paraplegias: A Comprehensive Overview.Front Mol Biosci. 2021 Nov 26;8:690899. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2021.690899. eCollection 2021. Front Mol Biosci. 2021. PMID: 34901147 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Lipids and synaptic functions.J Inherit Metab Dis. 2018 Nov;41(6):1117-1122. doi: 10.1007/s10545-018-0204-1. Epub 2018 Jun 4. J Inherit Metab Dis. 2018. PMID: 29869164 Review.
-
Impairment of brain and muscle energy metabolism detected by magnetic resonance spectroscopy in hereditary spastic paraparesis type 28 patients with DDHD1 mutations.J Neurol. 2014 Sep;261(9):1789-93. doi: 10.1007/s00415-014-7418-4. Epub 2014 Jul 3. J Neurol. 2014. PMID: 24989667
References
-
- Kenwrick S., Ionasescu V., Ionasescu G., Searby C., King A., Dubowitz M., Davies K.E. Linkage studies of X-linked recessive spastic paraplegia using DNA probes. Hum. Genet. 1986;73:264–266. - PubMed
-
- Schüle R., Schöls L. Genetics of hereditary spastic paraplegias. Semin. Neurol. 2011;31:484–493. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

