A ribosome-bound quality control complex triggers degradation of nascent peptides and signals translation stress
- PMID: 23178123
- PMCID: PMC3534965
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2012.10.044
A ribosome-bound quality control complex triggers degradation of nascent peptides and signals translation stress
Abstract
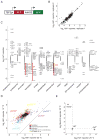
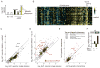
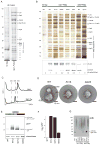
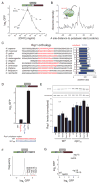
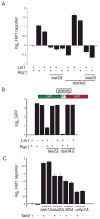
The conserved transcriptional regulator heat shock factor 1 (Hsf1) is a key sensor of proteotoxic and other stress in the eukaryotic cytosol. We surveyed Hsf1 activity in a genome-wide loss-of-function library in Saccaromyces cerevisiae as well as ~78,000 double mutants and found Hsf1 activity to be modulated by highly diverse stresses. These included disruption of a ribosome-bound complex we named the Ribosome Quality Control Complex (RQC) comprising the Ltn1 E3 ubiquitin ligase, two highly conserved but poorly characterized proteins (Tae2 and Rqc1), and Cdc48 and its cofactors. Electron microscopy and biochemical analyses revealed that the RQC forms a stable complex with 60S ribosomal subunits containing stalled polypeptides and triggers their degradation. A negative feedback loop regulates the RQC, and Hsf1 senses an RQC-mediated translation-stress signal distinctly from other stresses. Our work reveals the range of stresses Hsf1 monitors and elucidates a conserved cotranslational protein quality control mechanism.
Copyright © 2012 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

Comment in
-
Protein degradation: ensuring quality at the ribosome.Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2013 Jan;14(1):1. doi: 10.1038/nrm3499. Epub 2012 Dec 12. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2013. PMID: 23232563 No abstract available.
References
-
- Albanese V, Yam AY, Baughman J, Parnot C, Frydman J. Systems analyses reveal two chaperone networks with distinct functions in eukaryotic cells. Cell. 2006;124:75–88. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

