Posttranscriptional gene regulation by long noncoding RNA
- PMID: 23178169
- PMCID: PMC3594629
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jmb.2012.11.024
Posttranscriptional gene regulation by long noncoding RNA
Abstract
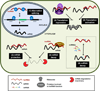
Eukaryotic cells transcribe a vast number of noncoding RNA species. Among them, long noncoding RNAs (lncRNAs) have been widely implicated in the regulation of gene transcription. However, examples of posttranscriptional gene regulation by lncRNAs are emerging. Through extended base-pairing, lncRNAs can stabilize or promote the translation of target mRNAs, while partial base-pairing facilitates mRNA decay or inhibits target mRNA translation. In the absence of complementarity, lncRNAs can suppress precursor mRNA splicing and translation by acting as decoys of RNA-binding proteins or microRNAs and can compete for microRNA-mediated inhibition leading to increased expression of the mRNA. Through these regulatory mechanisms, lncRNAs can elicit differentiation, proliferation, and cytoprotective programs, underscoring the rising recognition of lncRNA roles in human disease. In this review, we summarize the mechanisms of posttranscriptional gene regulation by lncRNAs identified until now.
Keywords: BACE1; PABP; RNA-binding protein; lincRNA; lncRNA; long noncoding RNA; mRNA turnover; poly(A)-binding protein; pre-mRNA; precursor mRNA; small nucleolar lncRNA; sno-lncRNA; translational regulation; β amyloid-cleaving enzyme 1.
Published by Elsevier Ltd.
Figures
References
-
- Kapranov P, Cheng J, Dike S, Nix DA, Duttagupta R, Willingham AT, et al. RNA maps reveal new RNA classes and a possible function for pervasive transcription. Science. 2007;316:1484–1488. - PubMed
-
- Barski A, Cuddapah S, Cui K, Roh TY, Schones DE, Wang Z, et al. Highresolution profiling of histone methylations in the human genome. Cell. 2007;129:823–837. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

