APLF promotes the assembly and activity of non-homologous end joining protein complexes
- PMID: 23178593
- PMCID: PMC3545299
- DOI: 10.1038/emboj.2012.304
APLF promotes the assembly and activity of non-homologous end joining protein complexes
Abstract
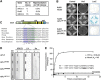
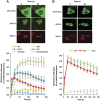
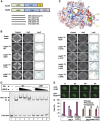
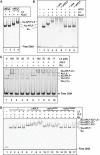
Non-homologous end joining (NHEJ) is critical for the maintenance of genetic integrity and DNA double-strand break (DSB) repair. NHEJ is regulated by a series of interactions between core components of the pathway, including Ku heterodimer, XLF/Cernunnos, and XRCC4/DNA Ligase 4 (Lig4). However, the mechanisms by which these proteins assemble into functional protein-DNA complexes are not fully understood. Here, we show that the von Willebrand (vWA) domain of Ku80 fulfills a critical role in this process by recruiting Aprataxin-and-PNK-Like Factor (APLF) into Ku-DNA complexes. APLF, in turn, functions as a scaffold protein and promotes the recruitment and/or retention of XRCC4-Lig4 and XLF, thereby assembling multi-protein Ku complexes capable of efficient DNA ligation in vitro and in cells. Disruption of the interactions between APLF and either Ku80 or XRCC4-Lig4 disrupts the assembly and activity of Ku complexes, and confers cellular hypersensitivity and reduced rates of chromosomal DSB repair in avian and human cells, respectively. Collectively, these data identify a role for the vWA domain of Ku80 and a molecular mechanism by which DNA ligase proficient complexes are assembled during NHEJ in mammalian cells, and reveal APLF to be a structural component of this critical DSB repair pathway.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures

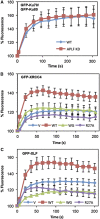
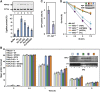

References
-
- Ahel I, Ahel D, Matsusaka T, Clark AJ, Pines J, Boulton SJ, West SC (2008) Poly(ADP-ribose)-binding zinc finger motifs in DNA repair/checkpoint proteins. Nature 451: 81–85 - PubMed
-
- Ahnesorg P, Smith P, Jackson SP (2006) XLF interacts with the XRCC4-DNA ligase IV complex to promote DNA nonhomologous end-joining. Cell 124: 301–313 - PubMed
-
- Arosio D, Cui S, Ortega C, Chovanec M, Di Marco S, Baldini G, Falaschi A, Vindigni A (2002) Studies on the mode of Ku interaction with DNA. J Biol Chem 277: 9741–9748 - PubMed
-
- Bekker-Jensen S, Fugger K, Danielsen JR, Gromova I, Sehested M, Celis J, Bartek J, Lukas J, Mailand N (2007) Human Xip1 (C2orf13) is a novel regulator of cellular responses to DNA strand breaks. J Biol Chem 282: 19638–19643 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

