Gut bacteria-host metabolic interplay during conventionalisation of the mouse germfree colon
- PMID: 23178667
- PMCID: PMC3603396
- DOI: 10.1038/ismej.2012.142
Gut bacteria-host metabolic interplay during conventionalisation of the mouse germfree colon
Abstract
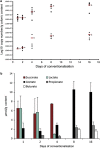
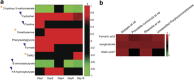
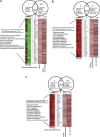
The interplay between dietary nutrients, gut microbiota and mammalian host tissues of the gastrointestinal tract is recognised as highly relevant for host health. Combined transcriptome, metabonome and microbial profiling tools were employed to analyse the dynamic responses of germfree mouse colonic mucosa to colonisation by normal mouse microbiota (conventionalisation) at different time-points during 16 days. The colonising microbiota showed a shift from early (days 1 and 2) to later colonisers (days 8 and 16). The dynamic changes in the microbial community were rapidly reflected by the urine metabolic profiles (day 1) and at later stages (day 4 onward) by the colon mucosa transcriptome and metabolic profiles. Correlations of host transcriptomes, metabolite patterns and microbiota composition revealed associations between Bacilli and Proteobacteria, and differential expression of host genes involved in energy and anabolic metabolism. Differential gene expression correlated with scyllo- and myo-inositol, glutamine, glycine and alanine levels in colonic tissues during the time span of conventionalisation. Our combined time-resolved analyses may help to expand the understanding of host-microbe molecular interactions during the microbial establishment.
Figures



References
-
- Ben-Dov E, Brenner A, Kushmaro A. Quantification of sulfate-reducing bacteria in industrial wastewater, by real-time polymerase chain reaction (PCR) using dsrA and apsA genes. Microb Ecol. 2007;54:439–451. - PubMed
-
- Bjursell M, Admyre T, Göransson M, Marley AE, Smith DM, Oscarsson J, et al. Improved glucose control and reduced body fat mass in free fatty acid receptor 2-deficient mice fed a high-fat diet. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2011;300:E211–E220. - PubMed
-
- Brown AJ, Goldsworthy SM, Barnes AA, Eilert MM, Tcheang L, Daniels D, et al. The orphan G protein-coupled receptors GPR41 and GPR43 are activated by propionate and other short chain carboxylic acids. J Biol Chem. 2003;278:11312–11319. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

