Enabling stem cell therapies for tissue repair: current and future challenges
- PMID: 23178704
- PMCID: PMC3620919
- DOI: 10.1016/j.biotechadv.2012.11.006
Enabling stem cell therapies for tissue repair: current and future challenges
Abstract
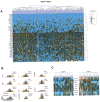
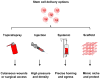
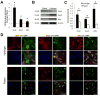
Stem cells embody the tremendous potential of the human body to develop, grow, and repair throughout life. Understanding the biologic mechanisms that underlie stem cell-mediated tissue regeneration is key to harnessing this potential. Recent advances in molecular biology, genetic engineering, and material science have broadened our understanding of stem cells and helped bring them closer to widespread clinical application. Specifically, innovative approaches to optimize how stem cells are identified, isolated, grown, and utilized will help translate these advances into effective clinical therapies. Although there is growing interest in stem cells worldwide, this enthusiasm must be tempered by the fact that these treatments remain for the most part clinically unproven. Future challenges include refining the therapeutic manipulation of stem cells, validating these technologies in randomized clinical trials, and regulating the global expansion of regenerative stem cell therapies.
Copyright © 2012 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures


References
-
- Guidelines for the Clinical Treatment of Stem Cells. International Society for Stem Cell Research Task Force. 2008
-
- Arien-Zakay H, Lecht S, Perets A, Roszell B, Lelkes PI, Lazarovici P. Quantitative assessment of neuronal differentiation in three-dimensional collagen gels using enhanced green fluorescence protein expressing PC12 pheochromocytoma cells. J Mol Neurosci. 2009;37:225–37. - PubMed
-
- Atiyeh BS, Costagliola M. Cultured epithelial autograft (CEA) in burn treatment: three decades later. Burns. 2007;33:405–13. - PubMed
-
- Baker M. Stem-cell pioneer bows out. Nature. 2011;479:459. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

