Molecular targets for treatment of kidney fibrosis
- PMID: 23179685
- PMCID: PMC3594378
- DOI: 10.1007/s00109-012-0983-z
Molecular targets for treatment of kidney fibrosis
Abstract
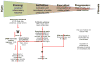
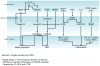
Renal fibrosis is the culmination of processes driven by signaling pathways involving transforming growth factor-β family of cytokines, connective-tissue growth factor, nuclear factor κB, Wnt/β-catenin, Notch, and other growth factors. Many studies in experimental animal models have directly targeted these pathways and demonstrated efficacy in mitigating renal fibrosis. However, only a small fraction of these approaches have been attempted in human and even fewer have been successfully translated to clinical use for patient with kidney diseases. Drugs with proven efficacy for treatment of kidney diseases and tissue fibrosis exert some of their effects by interfering with components of these pathways. This review considers key molecular mediators of renal fibrosis and their potential as targets for treatment of renal fibrosis.
Figures

References
-
- Harris RC, Neilson EG. Toward a unified theory of renal progression. Annual review of medicine. 2006;57:365–380. - PubMed
-
- Striker GE, Schainuck LI, Cutler RE, Benditt EP. Structural-functional correlations in renal disease. I. A method for assaying and classifying histopathologic changes in renal disease. Human pathology. 1970;1:615–630. - PubMed
-
- Nath KA. Tubulointerstitial changes as a major determinant in the progression of renal damage. American journal of kidney diseases : the official journal of the National Kidney Foundation. 1992;20:1–17. - PubMed
-
- Mackensen-Haen S, Bader R, Grund KE, Bohle A. Correlations between renal cortical interstitial fibrosis, atrophy of the proximal tubules and impairment of the glomerular filtration rate. Clinical nephrology. 1981;15:167–171. - PubMed
-
- Boor P, Sebekova K, Ostendorf T, Floege J. Treatment targets in renal fibrosis. Nephrology, dialysis, transplantation : official publication of the European Dialysis and Transplant Association - European Renal Association. 2007;22:3391–3407. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

