Isolation and culture of skeletal muscle myofibers as a means to analyze satellite cells
- PMID: 23179849
- PMCID: PMC3633469
- DOI: 10.1007/978-1-62703-128-8_28
Isolation and culture of skeletal muscle myofibers as a means to analyze satellite cells
Abstract
Multinucleated myofibers are the functional contractile units of skeletal muscle. In adult muscle, mononuclear satellite cells, located between the basal lamina and the plasmalemma of the myofiber, are the primary myogenic stem cells. This chapter describes protocols for isolation, culturing, and immunostaining of myofibers from mouse skeletal muscle. Myofibers are isolated intact and retain their associated satellite cells. The first protocol discusses myofiber isolation from the flexor digitorum brevis (FDB) muscle. These short myofibers are cultured in dishes coated with PureCol collagen (formerly known as Vitrogen) using a serum replacement medium. Employing such culture conditions, satellite cells remain associated with the myofibers, undergoing proliferation and differentiation on the myofiber surface. The second protocol discusses the isolation of longer myofibers from the extensor digitorum longus (EDL) muscle. Different from the FDB preparation, where multiple myofibers are processed together, the longer EDL myofibers are typically processed and cultured individually in dishes coated with Matrigel using a growth factor rich medium. Under these conditions, satellite cells initially remain associated with the parent myofiber and later migrate away, giving rise to proliferating and differentiating progeny. Myofibers from other types of muscles, such as diaphragm, masseter, and extraocular muscles can also be isolated and analyzed using protocols described herein. Overall, cultures of isolated myofibers provide essential tools for studying the interplay between the parent myofiber and its associated satellite cells. The current chapter provides background, procedural, and reagent updates, and step-by-step images of FDB and EDL muscle isolations, not included in our 2005 publication in this series.
Figures

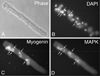

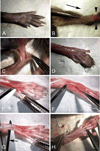
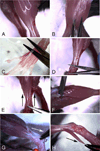
Similar articles
-
Isolation, Culture, and Immunostaining of Skeletal Muscle Myofibers from Wildtype and Nestin-GFP Mice as a Means to Analyze Satellite Cell.Methods Mol Biol. 2017;1556:51-102. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4939-6771-1_4. Methods Mol Biol. 2017. PMID: 28247345
-
Isolation and culture of skeletal muscle myofibers as a means to analyze satellite cells.Methods Mol Biol. 2005;290:281-304. doi: 10.1385/1-59259-838-2:281. Methods Mol Biol. 2005. PMID: 15361669 Free PMC article.
-
Isolation and culture of individual myofibers and their satellite cells from adult skeletal muscle.J Vis Exp. 2013 Mar 22;(73):e50074. doi: 10.3791/50074. J Vis Exp. 2013. PMID: 23542587 Free PMC article.
-
Defining the transcriptional signature of skeletal muscle stem cells.J Anim Sci. 2008 Apr;86(14 Suppl):E207-16. doi: 10.2527/jas.2007-0473. Epub 2007 Sep 18. J Anim Sci. 2008. PMID: 17878281 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Dormancy and quiescence of skeletal muscle stem cells.Results Probl Cell Differ. 2015;56:215-35. doi: 10.1007/978-3-662-44608-9_10. Results Probl Cell Differ. 2015. PMID: 25344673 Review.
Cited by
-
ANKK1 is found in myogenic precursors and muscle fibers subtypes with glycolytic metabolism.PLoS One. 2018 May 14;13(5):e0197254. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0197254. eCollection 2018. PLoS One. 2018. PMID: 29758057 Free PMC article.
-
Muscle Progenitors Derived from Extraocular Muscles Express Higher Levels of Neurotrophins and their Receptors than other Cranial and Limb Muscles.Cells. 2020 Mar 18;9(3):747. doi: 10.3390/cells9030747. Cells. 2020. PMID: 32197508 Free PMC article.
-
Primary Murine Myotubes as a Model for Investigating Muscular Dystrophy.Biomed Res Int. 2015;2015:594751. doi: 10.1155/2015/594751. Epub 2015 Aug 24. Biomed Res Int. 2015. PMID: 26380282 Free PMC article.
-
Isolation of Muscle Stem Cells from Mouse Skeletal Muscle.Methods Mol Biol. 2017;1556:23-39. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4939-6771-1_2. Methods Mol Biol. 2017. PMID: 28247343
-
Skeletal muscle satellite cells: background and methods for isolation and analysis in a primary culture system.Methods Mol Biol. 2012;798:21-52. doi: 10.1007/978-1-61779-343-1_2. Methods Mol Biol. 2012. PMID: 22130829 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hawke TJ, Garry DJ. Myogenic satellite cells: physiology to molecular biology. J Appl Physiol. 2001;91:534–551. - PubMed
-
- Zammit PS, Partridge TA, Yablonka-Reuveni Z. The skeletal muscle satellite cell: the stem cell that came in from the cold. J Histochem Cytochem. 2006;54:1177–1191. - PubMed
-
- Collins CA, Olsen I, Zammit PS, Heslop L, Petrie A, Partridge TA, Morgan JE. Stem cell function, self-renewal, and behavioral heterogeneity of cells from the adult muscle satellite cell niche. Cell. 2005;122:289–301. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

