The effect of posterior spinal fusion on respiratory function in Duchenne muscular dystrophy
- PMID: 23179984
- PMCID: PMC3555614
- DOI: 10.1007/s00586-012-2585-4
The effect of posterior spinal fusion on respiratory function in Duchenne muscular dystrophy
Abstract
Purpose: Posterior instrumented spinal fusion is indicated for progressive scoliosis that develops in Duchenne muscular dystrophy (DMD) patients. Whilst spinal fusion is known to improve quality of life, there is inconsistency amongst the literature regarding its specific effect on respiratory function. Our objective was to determine the effect of scoliosis correction by posterior spinal fusion on respiratory function in a large cohort of patients with DMD. Patients with DMD undergoing posterior spinal fusion were compared to patients with DMD not undergoing surgical intervention.
Methods: An observational study of 65 patients with DMD associated scoliosis, born between 1961 and 2001: 28 of which underwent correction of scoliosis via posterior spinal fusion (Surgical Group) and 37 of which did not undergo surgical intervention (Non-Surgical Group). Pulmonary function was assessed using traditional spirometry. Comparisons were made between groups at set times, and by way of rates of change over time.
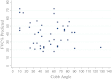
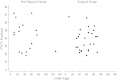
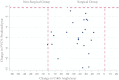
Results: There was no correlation between the level of respiratory dysfunction and the severity of scoliosis (as measured by Cobb angle) for the whole cohort. The Surgical Group had significantly worse respiratory function at a comparable age pre-operatively compared to the Non-Surgical Group, as measured by per cent predicted forced vital capacity (p = 0.02) on spirometry. The rate of decline of forced vital capacity and per cent predicted forced vital capacity was not slowed following surgery compared to the non-operated cases. There was no significant difference in survival between the two groups.
Conclusions: Severity of scoliosis was not a key determinant of respiratory dysfunction. Posterior spinal fusion did not reduce the rate of respiratory function decline. These two points suggest that intrinsic respiratory muscle weakness is the main determinant of decline in respiratory function in DMD.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Posterior spinal fusion for scoliosis in duchenne muscular dystrophy diminishes the rate of respiratory decline.Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2007 Feb 15;32(4):459-65. doi: 10.1097/01.brs.0000255062.94744.52. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2007. PMID: 17304138
-
Long-term Follow-up of Pulmonary Function and Scoliosis in Patients With Duchenne's Muscular Dystrophy and Spinal Muscular Atrophy.J Pediatr Orthop. 2016 Jan;36(1):63-9. doi: 10.1097/BPO.0000000000000396. J Pediatr Orthop. 2016. PMID: 26642076
-
Tranexamic acid diminishes intraoperative blood loss and transfusion in spinal fusions for duchenne muscular dystrophy scoliosis.Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2007 Sep 15;32(20):2278-83. doi: 10.1097/BRS.0b013e31814cf139. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2007. PMID: 17873823
-
Survival of patients with Duchenne muscular dystrophy who underwent spinal deformity correction.Dev Med Child Neurol. 2024 Feb;66(2):187-194. doi: 10.1111/dmcn.15711. Epub 2023 Jul 21. Dev Med Child Neurol. 2024. PMID: 37482906 Review.
-
[Characteristics in the treatment of scoliosis in muscular diseases].Z Orthop Ihre Grenzgeb. 1997 Mar-Apr;135(2):95-105. doi: 10.1055/s-2008-1039563. Z Orthop Ihre Grenzgeb. 1997. PMID: 9214180 Review. German.
Cited by
-
Safety and Efficacy of Treatment for Scolios Is Secondary to Spinal Muscular Atrophy Fused to Lumbar 5 Level.Spine Surg Relat Res. 2018 Apr 27;2(4):294-298. doi: 10.22603/ssrr.2017-0093. eCollection 2018 Oct 26. Spine Surg Relat Res. 2018. PMID: 31435537 Free PMC article.
-
Anesthesia and Perioperative Management for Surgical Correction of Neuromuscular Scoliosis in Children: A Narrative Review.J Clin Med. 2023 May 24;12(11):3651. doi: 10.3390/jcm12113651. J Clin Med. 2023. PMID: 37297846 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Clinical management of Duchenne muscular dystrophy: the state of the art.Neurol Sci. 2018 Nov;39(11):1837-1845. doi: 10.1007/s10072-018-3555-3. Epub 2018 Sep 14. Neurol Sci. 2018. PMID: 30218397 Review.
-
No difference in postoperative complication rates or cardiopulmonary function for early versus late scoliosis correction in Duchenne muscular dystrophy.Spine Deform. 2022 Nov;10(6):1429-1436. doi: 10.1007/s43390-022-00532-6. Epub 2022 Jun 13. Spine Deform. 2022. PMID: 35691977
-
Assessment and management of respiratory function in patients with Duchenne muscular dystrophy: current and emerging options.Ther Clin Risk Manag. 2015 Sep 28;11:1475-88. doi: 10.2147/TCRM.S55889. eCollection 2015. Ther Clin Risk Manag. 2015. PMID: 26451113 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Emery A, Muntoni F. Duchenne muscular dystrophy. Oxford: Oxford University Press; 2003.
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

