An HLA-DRB1-coded signal transduction ligand facilitates inflammatory arthritis: a new mechanism of autoimmunity
- PMID: 23180817
- PMCID: PMC3529776
- DOI: 10.4049/jimmunol.1202150
An HLA-DRB1-coded signal transduction ligand facilitates inflammatory arthritis: a new mechanism of autoimmunity
Abstract
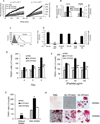
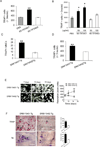
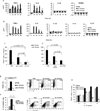
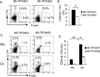
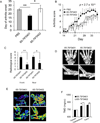
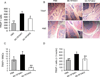
Particular alleles of HLA contribute to disease susceptibility and severity in many autoimmune conditions, but the mechanisms underlying these associations are often unknown. In this study, we demonstrate that the shared epitope (SE), an HLA-DRB1-coded sequence motif that is the single most significant genetic risk factor for erosive rheumatoid arthritis, acts as a signal transduction ligand that potently activates osteoclastogenesis, both in vitro and in vivo. The SE enhanced the production of several pro-osteoclastogenic factors and facilitated osteoclast (OC) differentiation in mouse and human cells in vitro. Transgenic mice expressing a human HLA-DRB1 allele that code the SE motif demonstrated markedly higher propensity for osteoclastogenesis and enhanced bone degradation capacity ex vivo. In addition, the SE enhanced the differentiation of Th17 cells expressing the receptor activator for NF-κB ligand. When the two agents were combined, IL-17 and the SE enhanced OC differentiation synergistically. When administered in vivo to mice with collagen-induced arthritis, the SE ligand significantly increased arthritis severity, synovial tissue OC abundance, and bone erosion. Thus, the SE contributes to arthritis severity by activating an OC-mediated bone-destructive pathway. These findings suggest that besides determining the target specificity of autoimmune responses, HLA molecules may influence disease outcomes by shaping the pathogenic consequences of such responses.
Figures
Comment in
-
New insights into functional effects of the shared epitope.Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2013 Jan;9(1):3. doi: 10.1038/nrrheum.2012.221. Epub 2012 Dec 11. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2013. PMID: 23229453 No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
A small shared epitope-mimetic compound potently accelerates osteoclast-mediated bone damage in autoimmune arthritis.J Immunol. 2013 Sep 1;191(5):2096-103. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1203231. Epub 2013 Jul 24. J Immunol. 2013. PMID: 23885107 Free PMC article.
-
Immune dysregulation by the rheumatoid arthritis shared epitope.J Immunol. 2010 Aug 1;185(3):1927-34. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.0904002. Epub 2010 Jun 30. J Immunol. 2010. PMID: 20592276 Free PMC article.
-
Shared epitope-aryl hydrocarbon receptor crosstalk underlies the mechanism of gene-environment interaction in autoimmune arthritis.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2018 May 1;115(18):4755-4760. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1722124115. Epub 2018 Apr 16. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2018. PMID: 29666259 Free PMC article.
-
Associations of human leukocyte antigens with autoimmune diseases: challenges in identifying the mechanism.J Hum Genet. 2015 Nov;60(11):697-702. doi: 10.1038/jhg.2015.100. Epub 2015 Aug 20. J Hum Genet. 2015. PMID: 26290149 Review.
-
New insights into the functional role of the rheumatoid arthritis shared epitope.FEBS Lett. 2011 Dec 1;585(23):3619-26. doi: 10.1016/j.febslet.2011.03.035. Epub 2011 Mar 22. FEBS Lett. 2011. PMID: 21420962 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
HLA-DRB1 the notorious gene in the mosaic of autoimmunity.Immunol Res. 2017 Feb;65(1):82-98. doi: 10.1007/s12026-016-8817-7. Immunol Res. 2017. PMID: 27435705
-
Basement membranes and autoimmune diseases.Matrix Biol. 2017 Jan;57-58:149-168. doi: 10.1016/j.matbio.2016.07.008. Epub 2016 Aug 2. Matrix Biol. 2017. PMID: 27496347 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The quest for better understanding of HLA-disease association: scenes from a road less travelled by.Discov Med. 2013 Sep;16(87):93-101. Discov Med. 2013. PMID: 23998445 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Shared epitope-antagonistic ligands: a new therapeutic strategy in mice with erosive arthritis.Arthritis Rheumatol. 2015 May;67(8):2061-70. doi: 10.1002/art.39158. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2015. PMID: 25892196 Free PMC article.
-
Indigenous Nigeria medicinal herbal remedies: A potential source for therapeutic against rheumatoid arthritis.Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2022 Jul;247(13):1148-1178. doi: 10.1177/15353702221102901. Epub 2022 Jun 16. Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2022. PMID: 35708153 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Klein J, Sato A. The HLA system. Second of two parts. N. Eng. J. Med. 2000;343:782–786. - PubMed
-
- Bromley M, Woolley DE. Histopathology of the rheumatoid lesion. Identification of cell types at sites of cartilage erosion. Arthritis Rheum. 1984;27:857–863. - PubMed
-
- Fujikawa Y, Shingu M, Torisu T, Itonaga I, Masumi S. Bone resorption by tartrate-resistant acid phosphatase-positive multinuclear cells isolated from rheumatoid synovium. Br J Rheumatol. 1996;35:213–217. - PubMed
-
- Gravallese EM, Manning C, Tsay A, et al. Synovial tissue in rheumatoid arthritis is a source of osteoclast differentiation factor. Arthritis Rheum. 2000;43:250–258. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

