Management strategies of Barrett's esophagus
- PMID: 23180941
- PMCID: PMC3501769
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v18.i43.6216
Management strategies of Barrett's esophagus
Abstract
Barrett's esophagus is a condition resulting from chronic gastro-esophageal reflux disease with a documented risk of esophageal adenocarcinoma. Current strategies for improved survival in patients with Barrett's adenocarcinoma focus on detection of dysplasia. This can be obtained by screening programs in high-risk cohorts of patients and/or endoscopic biopsy surveillance of patients with known Barrett's esophagus (BE). Several therapies have been developed in attempts to reverse BE and reduce cancer risk. Aggressive medical management of acid reflux, lifestyle modifications, antireflux surgery, and endoscopic treatments have been recommended for many patients with BE. Whether these interventions are cost-effective or reduce mortality from esophageal cancer remains controversial. Current treatment requires combinations of endoscopic mucosal resection techniques to eliminate visible lesions followed by ablation of residual metaplastic tissue. Esophagectomy is currently indicated in multifocal high-grade neoplasia or mucosal Barrett's carcinoma which cannot be managed by endoscopic approach.
Keywords: Barrett’s esophagus; Diagnosis; Esophageal adenocarcinoma; Esophagectomy; Management strategies.
Figures
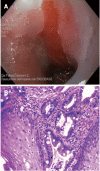
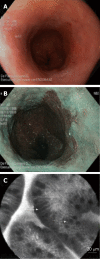
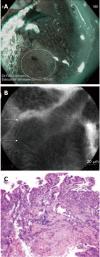
Similar articles
-
GERD and Barrett's esophagus: diagnostic and management strategies in the geriatric population.Geriatrics. 2009 Jul;64(7):9-12. Geriatrics. 2009. PMID: 19586085
-
Diagnosis and treatment of Barrett's oesophagus. A general survey.Acta Chir Belg. 2001 Mar-Apr;101(2):53-8. Acta Chir Belg. 2001. PMID: 11396051 Review.
-
The treatment of Barrett's esophagus.J Med Life. 2009 Jul-Sep;2(3):241-8. J Med Life. 2009. PMID: 20112466 Free PMC article. Review.
-
[Gastroesophageal reflux disease and malignancy].Rev Prat. 2008 Sep 15;58(13):1414-5, 1417, 1419-20. Rev Prat. 2008. PMID: 18924321 French.
-
Gastroesophageal reflux disease: From heartburn to cancer.World J Gastroenterol. 2010 Aug 14;16(30):3743-4. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v16.i30.3743. World J Gastroenterol. 2010. PMID: 20698034 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Radical excision of Barrett's esophagus and complete recovery of normal squamous epithelium.World J Gastroenterol. 2013 Aug 21;19(31):5195-8. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i31.5195. World J Gastroenterol. 2013. PMID: 23964158 Free PMC article.
-
Endoscopic Diagnosis and Management of Barrett's Esophagus with Low-Grade Dysplasia.Diagnostics (Basel). 2022 May 23;12(5):1295. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics12051295. Diagnostics (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35626450 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Endoscopic Findings of Gastro-Esophageal Reflux Disease in Elderly and Younger Age Groups.Front Med (Lausanne). 2021 Dec 10;8:606205. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2021.606205. eCollection 2021. Front Med (Lausanne). 2021. PMID: 34957130 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Sampliner RE. Updated guidelines for the diagnosis, surveillance, and therapy of Barrett’s esophagus. Am J Gastroenterol. 2002;97:1888–1895. - PubMed
-
- Spechler SJ, Sharma P, Souza RF, Inadomi JM, Shaheen NJ. American Gastroenterological Association medical position statement on the management of Barrett’s esophagus. Gastroenterology. 2011;140:1084–1091. - PubMed
-
- Wang KK, Sampliner RE. Updated guidelines 2008 for the diagnosis, surveillance and therapy of Barrett’s esophagus. Am J Gastroenterol. 2008;103:788–797. - PubMed
-
- Sharma P, McQuaid K, Dent J, Fennerty MB, Sampliner R, Spechler S, Cameron A, Corley D, Falk G, Goldblum J, et al. A critical review of the diagnosis and management of Barrett’s esophagus: the AGA Chicago Workshop. Gastroenterology. 2004;127:310–330. - PubMed
-
- Hirota WK, Zuckerman MJ, Adler DG, Davila RE, Egan J, Leighton JA, Qureshi WA, Rajan E, Fanelli R, Wheeler-Harbaugh J, et al. ASGE guideline: the role of endoscopy in the surveillance of premalignant conditions of the upper GI tract. Gastrointest Endosc. 2006;63:570–580. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Supplementary concepts
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

