Role of ABC transporters in the pathogenesis of Alzheimer's disease
- PMID: 23181169
- PMCID: PMC3504479
- DOI: 10.1021/cn300077c
Role of ABC transporters in the pathogenesis of Alzheimer's disease
Abstract
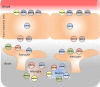
Alzheimer's disease (AD) is a progressive neurodegenerative disorder and the most common form of age-related dementia that begins with memory loss and progresses to include severe cognitive impairment. A major pathological hallmark of AD is the accumulation of beta amyloid peptide (Aβ) in senile plaques in the brain of AD patients. The exact mechanism by which AD takes place remains unknown. However, an increasing number of studies suggests that ATP-binding cassette (ABC) transporters, which are localized on the surface of brain endothelial cells of the blood-brain barrier (BBB) and brain parenchyma, may contribute to the pathogenesis of AD. Recent studies have unraveled important roles of ABC transporters including ABCB1 (P-glycoprotein, P-gp), ABCG2 (breast cancer resistant protein, BCRP), ABCC1 (multidrug resistance protein 1, MRP1), and the cholesterol transporter ABCA1 in the pathogenesis of AD and Aβ peptides deposition inside the brain. Therefore, understanding the mechanisms by which these transporters contribute to Aβ deposition in the brain is important for the development of new therapeutic strategies against AD. This review summarizes and highlights the accumulating evidence in the literature which describe the role of altered function of various ABC transporters in the pathogenesis and progression of AD and the implications of modulating their functions for the treatment of AD.
Figures

References
-
- de Souza L. C.; Sarazin M.; Goetz C.; Dubois B. (2009) Clinical investigations in primary care. Front. Neurol. Neurosci. 24, 1–11. - PubMed
-
- Selkoe D. J. (2001) Alzheimer’s disease: genes, proteins, and therapy. Physiol. Rev. 81, 741–766. - PubMed
-
- Mozar H. N.; Bal D. G.; Howard J. T. (1987) Perspectives on the etiology of Alzheimer’s disease. JAMA, J. Am. Med. Assoc. 257, 1503–1507. - PubMed
-
- Hebert L. E.; Scherr P. A.; Bienias J. L.; Bennett D. A.; Evans D. A. (2004) State-specific projections through 2025 of Alzheimer disease prevalence. Neurology 62, 1645. - PubMed
-
- Massoud F.; Leger G. C. (2011) Pharmacological treatment of Alzheimer disease. Can. J. Psychiatry 56, 579–588. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

