A study of atherosclerosis in patients with chronic renal failure with special reference to carotid artery intima media thickness
- PMID: 23181176
- PMCID: PMC3503361
- DOI: 10.4103/1995-705X.102147
A study of atherosclerosis in patients with chronic renal failure with special reference to carotid artery intima media thickness
Abstract
Objectives: Cardiovascular disease is the leading cause of morbidity and mortality in patients with chronic renal failure (CRF). This study attempts to identify the factors responsible for atherosclerosis in CRF patients using carotid artery intima media thickness (CAIMT) as a surrogate marker of atherosclerosis.
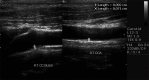
Materials and methods: CAIMT was measured by high-resolution B-mode ultrasonography in 100 CRF patients and 50 age- and sex-matched healthy controls. Data were analyzed by software SPSS (17(th) version) for Windows.
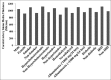
Results: CRF patients had a significantly higher CAIMT (1026.83 ± 17.19 micron, mean ± SE, P < 0.001) than age- and sex-matched healthy controls (722.46 ± 7.61 micron). There was inverse correlation between CAIMT and glomerular filtration rate (GFR) (P < 0.001) independent of traditional risk factors. There was also significant positive correlation between CAIMT and traditional risk factors of atherosclerosis. Ischemic heart disease (IHD) also showed positive correlation with CAIMT (P = 0.007) and inverse correlation with GFR (P = 0.005).
Conclusions: There is high prevalence of atherosclerosis in CRF patients. CAIMT can be used to detect and predict future incidence of IHD in CRF patients.
Keywords: Atherosclerosis; carotid artery intima media thickness; chronic renal failure; ischemic heart disease; traditional risk factors of atherosclerosis.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Carotid artery intima media thickness as a surrogate marker of atherosclerosis in patient with chronic renal failure on hemodialysis.N Am J Med Sci. 2012 Feb;4(2):77-80. doi: 10.4103/1947-2714.93379. N Am J Med Sci. 2012. PMID: 22408752 Free PMC article.
-
Measurement of intima media thickness of carotid artery by B-mode ultrasound in healthy people of India and Bangladesh, and relation of age and sex with carotid artery intima media thickness: An observational study.J Cardiovasc Dis Res. 2012 Apr;3(2):128-31. doi: 10.4103/0975-3583.95367. J Cardiovasc Dis Res. 2012. PMID: 22629031 Free PMC article.
-
Premature atherosclerosis in children with beta-thalassemia major: New diagnostic marker.BMC Pediatr. 2017 Mar 9;17(1):69. doi: 10.1186/s12887-017-0820-1. BMC Pediatr. 2017. PMID: 28279156 Free PMC article.
-
Homocystein and carotid atherosclerosis in chronic renal failure.Hippokratia. 2007 Oct;11(4):205-9. Hippokratia. 2007. PMID: 19582196 Free PMC article.
-
Increased carotid artery intima-media thickness in patients with tympanosclerosis: Common risk factors with atherosclerosis?Kaohsiung J Med Sci. 2015 Apr;31(4):199-202. doi: 10.1016/j.kjms.2015.01.003. Epub 2015 Feb 9. Kaohsiung J Med Sci. 2015. PMID: 25835276 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
A Control-Theoretic Model of Atherosclerosis.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Feb 12;20(3):785. doi: 10.3390/ijms20030785. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 30759798 Free PMC article.
-
Albuminuria but not low eGFR is closely associated with atherosclerosis in patients with type 2 diabetes: an observational study.Diabetol Metab Syndr. 2022 Apr 12;14(1):50. doi: 10.1186/s13098-022-00824-x. Diabetol Metab Syndr. 2022. PMID: 35413936 Free PMC article.
-
Correlation between nonalcoholic fatty liver and cardiovascular disease in elderly hemodialysis patients.Int Urol Nephrol. 2016 Jun;48(6):883-9. doi: 10.1007/s11255-016-1237-8. Epub 2016 Feb 23. Int Urol Nephrol. 2016. PMID: 26905407
-
Carotid Intima-Media Thickness: A Surrogate Marker for Cardiovascular Disease in Chronic Kidney Disease Patients.Clin Med Insights Cardiol. 2019 Jun 21;13:1179546819852941. doi: 10.1177/1179546819852941. eCollection 2019. Clin Med Insights Cardiol. 2019. PMID: 31258338 Free PMC article.
-
Coagulation activation, depletion of platelet granules and endothelial integrity in case of uraemia and haemodialysis treatment.BMC Nephrol. 2013 Mar 27;14:72. doi: 10.1186/1471-2369-14-72. BMC Nephrol. 2013. PMID: 23537104 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Foley RN, Parfrey PS, Sarnak MJ. Clinical epidemiology of cardiovascular disease in chronic renal disease. Am J Kidney Dis. 1998;32:S112–9. - PubMed
-
- Goodman WG, Goldin J, Kuizon BD, Yoon C, Gales B, Sider D, et al. Coronary-artery calcification in young adults with end-stage renal disease who are undergoing dialysis. N Engl J Med. 2000;342:1478–83. - PubMed
-
- Collins AJ, Li S, Gilbertson DT, Liu J, Chen SC, Herzog CA. Chronic kidney disease and cardiovascular disease in the medicare population. Kidney Int Suppl. 2003;64:S24–31. - PubMed
-
- Lorenz MW, Markus HS, Bots ML, Rosvall M, Sitzer M. Prediction of clinical cardiovascular events with carotid intima-media thickness.A systematic review and meta-analysis. Circulation. 2007;115:459–67. - PubMed
-
- Simon A, Gariepy J, Chironi G, Megnien JL, Levenson J. Intima-media thickness: A new tool for diagnosis and treatment of cardiovascular risk. J Hypertens. 2002;20:159–69. - PubMed