Theoretical investigation on structural, functional and epitope of a 12 kDa excretory-secretory protein from Toxoplasma gondii
- PMID: 23181504
- PMCID: PMC3542155
- DOI: 10.1186/1472-6807-12-30
Theoretical investigation on structural, functional and epitope of a 12 kDa excretory-secretory protein from Toxoplasma gondii
Abstract
Background: Toxoplasma gondii is an intracellular coccidian parasite that causes toxoplasmosis. It was estimated that more than one third of the world population is infected by T. gondii, and the disease is critical in fetuses and immunosuppressed patients. Thus, early detection is crucial for disease diagnosis and therapy. However, the current available toxoplasmosis diagnostic tests vary in their accuracy and the better ones are costly.
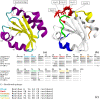
Results: An earlier published work discovered a highly antigenic 12 kDa excretory-secretory (ES) protein of T. gondii which may potentially be used for the development of an antigen detection test for toxoplasmosis. However, the three-dimensional structure of the protein is unknown. Since epitope identification is important prior to designing of a specific antibody for an antigen-detection based diagnostic test, the structural elucidation of this protein is essential. In this study, we constructed a three dimensional model of the 12 kDa ES protein. The built structure possesses a thioredoxin backbone which consists of four α-helices flanking five β-strands at the center. Three potential epitopes (6-8 residues) which can be combined into one "single" epitope have been identified from the built structure as the most potential antibody binding site.
Conclusion: Together with specific antibody design, this work could contribute towards future development of an antigen detection test for toxoplasmosis.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Crystal structure of the complex between the monomeric form of Toxoplasma gondii surface antigen 1 (SAG1) and a monoclonal antibody that mimics the human immune response.J Mol Biol. 2005 Nov 25;354(2):447-58. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2005.09.028. Epub 2005 Sep 30. J Mol Biol. 2005. PMID: 16242717
-
Toxoplasma gondii-Derived Synthetic Peptides Containing B- and T-Cell Epitopes from GRA2 Protein Are Able to Enhance Mice Survival in a Model of Experimental Toxoplasmosis.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2016 Jun 1;6:59. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2016.00059. eCollection 2016. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2016. PMID: 27313992 Free PMC article.
-
GRA7, an excretory 29 kDa Toxoplasma gondii dense granule antigen released by infected host cells.Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1998 Mar 15;91(2):251-62. doi: 10.1016/s0166-6851(97)00227-2. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1998. PMID: 9566518
-
Candidate antigenic epitopes for vaccination and diagnosis strategies of Toxoplasma gondii infection: A review.Microb Pathog. 2019 Dec;137:103788. doi: 10.1016/j.micpath.2019.103788. Epub 2019 Oct 9. Microb Pathog. 2019. PMID: 31605758 Review.
-
[Development of immunological antigen for detecting Toxoplasma gondii infection].Zhongguo Xue Xi Chong Bing Fang Zhi Za Zhi. 2011 Oct;23(5):590-4. Zhongguo Xue Xi Chong Bing Fang Zhi Za Zhi. 2011. PMID: 22263520 Review. Chinese.
Cited by
-
Minireview: applied structural bioinformatics in proteomics.Protein J. 2013 Oct;32(7):505-11. doi: 10.1007/s10930-013-9514-1. Protein J. 2013. PMID: 24096348 Review.
References
-
- Saadatnia G, Mohamed Z, Rifar FG, Osman E, Moghadam ZK, Noordin R. Toxoplasma gondii excretory secretory antigen protein of diagnostic potential. Acta Path Micro Im. 2011;120:47–55. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

