Evidence for the role of mast cells in colon-bladder cross organ sensitization
- PMID: 23182915
- PMCID: PMC3715122
- DOI: 10.1016/j.autneu.2012.09.002
Evidence for the role of mast cells in colon-bladder cross organ sensitization
Abstract
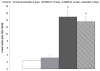
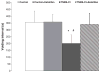
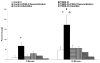
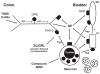
This study examined the contribution of mast cells to colon-bladder cross organ sensitization induced by colon irritation with trinitrobenzene sulfonic acid (TNBS-CI). In urethane anesthetized rats 12 days after TNBS-CI, the voiding interval was reduced from 357 s to 201 s and urothelial permeability, measured indirectly by absorption of sodium fluorescein from the bladder lumen, increased six-fold. These effects were blocked by oral administration of ketotifen (10 mg/kg, for 5 days), a mast cell stabilizing agent. TNBS-CI in wild type mice produced a similar decrease in voiding interval (from 319 s to 209 s) and a 10-fold increase in urothelial permeability; however this did not occur in KitªWª/KitªW-vª mast cell deficient mice. Contractile responses of bladder strips elicited by Compound 48/80 (50 μg/ml), a mast cell activating agent, were significantly larger in strips from rats with TNBS-CI (145% increase in baseline tension) than in control rats (55% increase). The contractions of strips from rats with TNBS-CI were reduced 80-90% by pretreatment of strips with ketotifen (20 μM), whereas contractions of strips from control animals were not significantly changed. Bladder strips were pretreated with SLIGRL-NH2 (100 μM) to desensitize PAR-2, the receptor for mast cell tryptase. SLIGRL-NH2 pretreatment reduced by 60-80% the 48/80 induced contractions in strips from rats with TNBS-CI but did not alter the contractions in strips from control rats. These data indicate that bladder mast cells contribute to the bladder dysfunction following colon-bladder cross-sensitization.
Copyright © 2012 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures

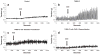


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

