Identification of proteins differentially expressed in adriamycin-resistant (pumc-91/ADM) and parental (pumc-91) human bladder cancer cell lines by proteome analysis
- PMID: 23183654
- PMCID: PMC11824256
- DOI: 10.1007/s00432-012-1350-8
Identification of proteins differentially expressed in adriamycin-resistant (pumc-91/ADM) and parental (pumc-91) human bladder cancer cell lines by proteome analysis
Abstract
Purpose: Resistance to chemotherapy drugs remains a difficult problem in bladder cancer treatment. Protein expression is an important factor underlying multidrug resistance (MDR) in bladder cancer. The aim of the study was to explore differentially expressed proteins responsible for MDR between an adriamycin-resistant human bladder cancer cell line (pumc-91/ADM) and its parental cell line (pumc-91).
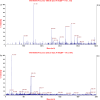
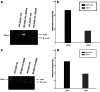
Methods: Two-dimensional gel electrophoresis (2-DE) combining image analysis was used to screen the differentially expressed protein spots between the pumc-91/ADM and pumc-91 cell lines. Then, the protein spots were identified using MALDI-TOF/TOF mass spectrometry. Among the identified proteins, annexin A2 (ANXA2) and nucleophosmin (NPM1) were then further verified using RT-PCR and Western blot analysis.
Results: A total of 30 proteins, including 19 up-regulated and 11 down-regulated proteins, were successfully identified in pumc-91/ADM. According to their different functions, these 30 proteins were classified into 12 categories. Annexin A2 (ANXA2) and nucleophosmin (NPM1) were up-regulated in pumc-91/ADM compared with pumc-91.
Conclusion: The proteins identified may have an important clinical significance in MDR, and ANXA2 and NPM1 may take part in mechanism of MDR in bladder cancer.
Conflict of interest statement
We declare that we have no conflict of interest.
Figures





References
-
- Baguley BC (2010) Multi-drug resistance in cancer. Methods Mol Biol 596:1–9 - PubMed
-
- Borer RA, Lehner CF, Eppenberger HM et al (1989) Major nucleolar proteins shuttle between nucleus and cytoplasm. Cell 56:379–390 - PubMed
-
- Bradford MM (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem 72:248–254 - PubMed
-
- Colombo E, Marine JC, Danovi D et al (2002) Nucleophosmin regulates the stability and transcriptional activity of p53. Nat Cell Biol 4:529–533 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

