Epigenetic regulation of miRNA-211 by MMP-9 governs glioma cell apoptosis, chemosensitivity and radiosensitivity
- PMID: 23183822
- PMCID: PMC3717804
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.683
Epigenetic regulation of miRNA-211 by MMP-9 governs glioma cell apoptosis, chemosensitivity and radiosensitivity
Abstract
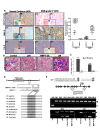
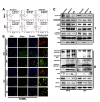
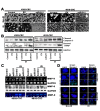
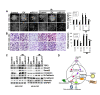
Glioblastoma multiforme (GBM) is the most aggressive brain cancer, and to date, no curative treatment has been developed. In this study, we report that miR-211, a microRNA predicted to target MMP-9, is suppressed in grade IV GBM specimens. Furthermore, we found that miR-211 suppression in GBM involves aberrant methylation-mediated epigenetic silencing of the miR-211 promoter. Indeed, we observed a highly significant inverse correlation between miR-211 expression and MMP-9 protein levels, which is indicative of post-transcriptional control of gene expression. Additionally, shRNA specific for MMP-9 (pM) promoted miR-211 expression via demethylation of miR-211 promoter-associated CpG islands (-140 to +56). In independent experiments, we confirmed that miR-211 overexpression and pM treatments led to the activation of the intrinsic mitochondrial/Caspase-9/3-mediated apoptotic pathway in both glioma cells and cancer stem cells (CSC). We also investigated whether miR-211 is involved in the regulation of MMP-9 and thus plays a functional role in GBM. We found an acute inhibitory effect of miR-211 on glioma cell invasion and migration via suppression of MMP-9. Given the insensitivity of some GBMs to radiation and chemotherapy (temozolomide) along with the hypothesis that glioma CSC cause resistance to therapy, our study indicates that miR-211 or pM in combination with ionizing radiation (IR) and temozolomide significantly induces apoptosis and DNA fragmentation. Of note, miR-211- and pM-treated CSC demonstrated increased drug retention capacity, as observed by MDR1/P-gp mediated-Rhodamine 123 drug efflux activity assay. These results suggest that either rescuing miR-211 expression or downregulation of MMP-9 may have a new therapeutic application for GBM patients in the future.
Conflict of interest statement
Authors declare no conflict of interest exists with this manuscript.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Identification of MMP-9 specific microRNA expression profile as potential targets of anti-invasion therapy in glioblastoma multiforme.Brain Res. 2011 Sep 9;1411:108-15. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2011.07.002. Epub 2011 Jul 13. Brain Res. 2011. PMID: 21831363
-
MicroRNA-128-3p Enhances the Chemosensitivity of Temozolomide in Glioblastoma by Targeting c-Met and EMT.Sci Rep. 2020 Jun 11;10(1):9471. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-65331-3. Sci Rep. 2020. PMID: 32528036 Free PMC article.
-
MiR-449a exerts tumor-suppressive functions in human glioblastoma by targeting Myc-associated zinc-finger protein.Mol Oncol. 2015 Mar;9(3):640-56. doi: 10.1016/j.molonc.2014.11.003. Epub 2014 Nov 20. Mol Oncol. 2015. PMID: 25487955 Free PMC article.
-
microRNAs: Potential glioblastoma radiosensitizer by targeting radiation-related molecular pathways.Mutat Res. 2019 Nov;816-818:111679. doi: 10.1016/j.mrfmmm.2019.111679. Epub 2019 Oct 21. Mutat Res. 2019. PMID: 31715522 Review.
-
Epigenetics of glioblastoma multiforme: From molecular mechanisms to therapeutic approaches.Semin Cancer Biol. 2022 Aug;83:100-120. doi: 10.1016/j.semcancer.2020.12.015. Epub 2020 Dec 25. Semin Cancer Biol. 2022. PMID: 33370605 Review.
Cited by
-
Simultaneous blockade of interacting CK2 and EGFR pathways by tumor-targeting nanobioconjugates increases therapeutic efficacy against glioblastoma multiforme.J Control Release. 2016 Dec 28;244(Pt A):14-23. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2016.11.001. Epub 2016 Nov 5. J Control Release. 2016. PMID: 27825958 Free PMC article.
-
Role of Mitochondria in Radiation Responses: Epigenetic, Metabolic, and Signaling Impacts.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Oct 13;22(20):11047. doi: 10.3390/ijms222011047. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34681703 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Extracellular Vesicles and MicroRNAs: Their Role in Tumorigenicity and Therapy for Brain Tumors.Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2016 Apr;36(3):361-76. doi: 10.1007/s10571-015-0293-4. Epub 2016 Mar 17. Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2016. PMID: 26983830 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Anticancer function of α-solanine in lung adenocarcinoma cells by inducing microRNA-138 expression.Tumour Biol. 2016 May;37(5):6437-46. doi: 10.1007/s13277-015-4528-2. Epub 2015 Dec 2. Tumour Biol. 2016. PMID: 26631041
-
Targeting miR-381-NEFL axis sensitizes glioblastoma cells to temozolomide by regulating stemness factors and multidrug resistance factors.Oncotarget. 2015 Feb 20;6(5):3147-64. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.3061. Oncotarget. 2015. PMID: 25605243 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Calin GA, Liu CG, Sevignani C, Ferracin M, Felli N, Dumitru CD, Shimizu M, Cimmino A, Zupo S, Dono M, Dell'Aquila ML, Alder H, Rassenti L, Kipps TJ, Bullrich F, Negrini M, et al. MicroRNA profiling reveals distinct signatures in B cell chronic lymphocytic leukemias. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2004;101:11755–60. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Jovanovic M, Hengartner MO. miRNAs and apoptosis: RNAs to die for. Oncogene. 2006;25:6176–87. - PubMed
-
- Kent OA, Mendell JT. A small piece in the cancer puzzle: microRNAs as tumor suppressors and oncogenes. Oncogene. 2006;25:6188–96. - PubMed
-
- Volinia S, Calin GA, Liu CG, Ambs S, Cimmino A, Petrocca F, Visone R, Iorio M, Roldo C, Ferracin M, Prueitt RL, Yanaihara N, Lanza G, Scarpa A, Vecchione A, Negrini M, et al. A microRNA expression signature of human solid tumors defines cancer gene targets. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006;103:2257–61. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Esquela-Kerscher A, Slack FJ. Oncomirs - microRNAs with a role in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 2006;6:259–69. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

