microRNA-independent recruitment of Argonaute 1 to nanos mRNA through the Smaug RNA-binding protein
- PMID: 23184089
- PMCID: PMC3537145
- DOI: 10.1038/embor.2012.192
microRNA-independent recruitment of Argonaute 1 to nanos mRNA through the Smaug RNA-binding protein
Abstract
Argonaute (Ago) proteins are typically recruited to target messenger RNAs via an associated small RNA such as a microRNA (miRNA). Here, we describe a new mechanism of Ago recruitment through the Drosophila Smaug RNA-binding protein. We show that Smaug interacts with the Ago1 protein, and that Ago1 interacts with and is required for the translational repression of the Smaug target, nanos mRNA. The Ago1/nanos mRNA interaction does not require a miRNA, but it does require Smaug. Taken together, our data suggest a model whereby Smaug directly recruits Ago1 to nanos mRNA in a miRNA-independent manner, thereby repressing translation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures
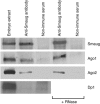

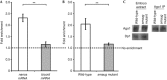
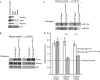

Comment in
-
Smaug: an unexpected journey into the mechanisms of post-transcriptional regulation.Fly (Austin). 2013 Jul-Sep;7(3):142-5. doi: 10.4161/fly.24336. Epub 2013 Mar 21. Fly (Austin). 2013. PMID: 23519205 Free PMC article.
Similar articles
-
Smaug: an unexpected journey into the mechanisms of post-transcriptional regulation.Fly (Austin). 2013 Jul-Sep;7(3):142-5. doi: 10.4161/fly.24336. Epub 2013 Mar 21. Fly (Austin). 2013. PMID: 23519205 Free PMC article.
-
smaug protein represses translation of unlocalized nanos mRNA in the Drosophila embryo.Genes Dev. 1996 Oct 15;10(20):2600-9. doi: 10.1101/gad.10.20.2600. Genes Dev. 1996. PMID: 8895661
-
Global regulation of mRNA translation and stability in the early Drosophila embryo by the Smaug RNA-binding protein.Genome Biol. 2014 Jan 7;15(1):R4. doi: 10.1186/gb-2014-15-1-r4. Genome Biol. 2014. PMID: 24393533 Free PMC article.
-
The role of GW182 proteins in miRNA-mediated gene silencing.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2013;768:147-63. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4614-5107-5_9. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2013. PMID: 23224969 Review.
-
MicroRNAs silence gene expression by repressing protein expression and/or by promoting mRNA decay.Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 2006;71:523-30. doi: 10.1101/sqb.2006.71.013. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 2006. PMID: 17381335 Review.
Cited by
-
Unambiguous identification of miRNA:target site interactions by different types of ligation reactions.Mol Cell. 2014 Jun 19;54(6):1042-1054. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2014.03.049. Epub 2014 May 22. Mol Cell. 2014. PMID: 24857550 Free PMC article.
-
Germ Plasm Biogenesis--An Oskar-Centric Perspective.Curr Top Dev Biol. 2016;116:679-707. doi: 10.1016/bs.ctdb.2015.11.024. Epub 2016 Feb 13. Curr Top Dev Biol. 2016. PMID: 26970648 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mammalian Argonaute-DNA binding?Biol Direct. 2014 Dec 4;10:27. doi: 10.1186/s13062-014-0027-4. Biol Direct. 2014. PMID: 25472905 Free PMC article.
-
Preferential microRNA targeting revealed by in vivo competitive binding and differential Argonaute immunoprecipitation.Nucleic Acids Res. 2017 Sep 29;45(17):10218-10228. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkx640. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017. PMID: 28973447 Free PMC article.
-
The maternal-to-zygotic transition: reprogramming of the cytoplasm and nucleus.Nat Rev Genet. 2025 Apr;26(4):245-267. doi: 10.1038/s41576-024-00792-0. Epub 2024 Nov 25. Nat Rev Genet. 2025. PMID: 39587307 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Hentze MW, Gebauer F, Preiss T (2007) Cis-regulatory sequences and trans-acting factors in translational control. In Translational Control in Biology and Medicine Mathews MB, Sonenberg N, Hershey JWB (eds), pp 269–295New York, USA: Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press,
-
- Smibert CA, Wilson JE, Kerr K, Macdonald PM (1996) Smaug protein represses translation of unlocalized nanos mRNA in the Drosophila embryo. Genes Dev 10: 2600–2609 - PubMed
-
- Dahanukar A, Walker JA, Wharton RP (1999) Smaug, a novel RNA-binding protein that operates a translational switch in Drosophila. Mol Cell 4: 209–218 - PubMed
-
- Aviv T, Lin Z, Lau S, Rendl LM, Sicheri F, Smibert CA (2003) The RNA-binding SAM domain of Smaug defines a new family of post-transcriptional regulators. Nat Struct Biol 10: 614–621 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

