MicroRNA-302 replacement therapy sensitizes breast cancer cells to ionizing radiation
- PMID: 23184229
- PMCID: PMC3594086
- DOI: 10.1007/s11095-012-0936-9
MicroRNA-302 replacement therapy sensitizes breast cancer cells to ionizing radiation
Abstract
Purpose: Solid tumors can be resistant or develop resistance to radiotherapy. The purpose of this study is to explore whether microRNA-302 is involved in radioresistance and can be exploited as a sensitizer to enhance sensitivity of breast cancer cells to radiation therapy.
Methods: MiR-302 expression levels in radioresistant cell lines were analyzed in comparison with their parent cell lines. Furthermore, we investigated whether enforced expression of miR-302 sensitized radioresistant breast cancer cells to ionizing radiation in vitro and in vivo.
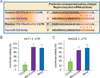
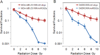
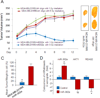
Results: MiR-302 was downregulated in irradiated breast cancer cells. Additionally, the expression levels of miR-302a were inversely correlated with those of AKT1 and RAD52, two critical regulators of radioresistance. More promisingly, miR-302a sensitized radioresistant breast cancer cells to radiation therapy in vitro and in vivo and reduced the expression of AKT1 and RAD52.
Conclusion: Our findings demonstrated that decreased expression of miR-302 confers radioresistance and restoration of miR-302 baseline expression sensitizes breast cancer cells to radiotherapy. These data suggest that miR-302 is a potential sensitizer to radiotherapy.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Inhibition of breast cancer metastasis with microRNA-302a by downregulation of CXCR4 expression.Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2014 Aug;146(3):535-42. doi: 10.1007/s10549-014-3053-0. Epub 2014 Jul 17. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2014. Retraction in: Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2022 Dec;196(3):665. doi: 10.1007/s10549-022-06779-x. PMID: 25030358 Retracted.
-
Radiation resistance due to high expression of miR-21 and G2/M checkpoint arrest in breast cancer cells.Radiat Oncol. 2012 Dec 5;7:206. doi: 10.1186/1748-717X-7-206. Radiat Oncol. 2012. PMID: 23216894 Free PMC article.
-
Tumor suppressor miR-29c regulates radioresistance in lung cancer cells.Tumour Biol. 2017 Mar;39(3):1010428317695010. doi: 10.1177/1010428317695010. Tumour Biol. 2017. PMID: 28345453
-
MicroRNA 23b regulates autophagy associated with radioresistance of pancreatic cancer cells.Gastroenterology. 2013 Nov;145(5):1133-1143.e12. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2013.07.048. Epub 2013 Aug 2. Gastroenterology. 2013. PMID: 23916944
-
Innovative therapeutic strategies to overcome radioresistance in breast cancer.Front Oncol. 2024 May 30;14:1379986. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2024.1379986. eCollection 2024. Front Oncol. 2024. PMID: 38873260 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
MicroRNAs in pathogenesis of breast cancer: Implications in diagnosis and treatment.World J Clin Oncol. 2014 May 10;5(2):48-60. doi: 10.5306/wjco.v5.i2.48. World J Clin Oncol. 2014. PMID: 24829851 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effects of AntagomiRs on Different Lung Diseases in Human, Cellular, and Animal Models.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Aug 13;20(16):3938. doi: 10.3390/ijms20163938. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31412612 Free PMC article.
-
Non-coding RNAs modulation in breast cancer radioresponse: mechanisms and therapeutic implications.Strahlenther Onkol. 2025 Jul;201(7):669-678. doi: 10.1007/s00066-024-02317-4. Epub 2024 Nov 15. Strahlenther Onkol. 2025. PMID: 39545960 Review.
-
Up-regulation of microRNA-302a inhibited the proliferation and invasion of colorectal cancer cells by regulation of the MAPK and PI3K/Akt signaling pathways.Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2015 May 1;8(5):4481-91. eCollection 2015. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2015. PMID: 26191138 Free PMC article.
-
Application of the microRNA-302/367 cluster in cancer therapy.Cancer Sci. 2020 Apr;111(4):1065-1075. doi: 10.1111/cas.14317. Epub 2020 Feb 13. Cancer Sci. 2020. PMID: 31957939 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Overgaard M. Radiotherapy as part of a multidisciplinary treatment strategy in early breast cancer. Eur J Cancer. 2001;37(Suppl 7):S33–S43. - PubMed
-
- Croce CM, Calin GA. miRNAs, cancer, and stem cell division. Cell. 2005;122(1):6–7. - PubMed
-
- Bartel DP. MicroRNAs: genomics, biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell. 2004;116(2):281–297. - PubMed
-
- Ambros V. microRNAs: tiny regulators with great potential. Cell. 2001;107(7):823–826. - PubMed
-
- Lu J, Getz G, Miska EA, Alvarez-Saavedra E, Lamb J, Peck D, et al. MicroRNA expression profiles classify human cancers. Nature. 2005;435(7043):834–838. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

