Angiotensin II-independent upregulation of cyclooxygenase-2 by activation of the (Pro)renin receptor in rat renal inner medullary cells
- PMID: 23184385
- PMCID: PMC3548040
- DOI: 10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.112.196303
Angiotensin II-independent upregulation of cyclooxygenase-2 by activation of the (Pro)renin receptor in rat renal inner medullary cells
Abstract
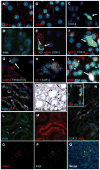
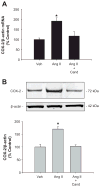
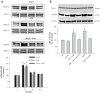
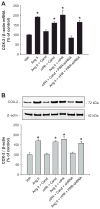
During renin-angiotensin system activation, cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2)-derived prostaglandins attenuate the pressor and antinatriuretic effects of angiotensin II (AngII) in the renal medulla. The (pro)renin receptor (PRR) is abundantly expressed in the collecting ducts (CD) and its expression is augmented by AngII. PRR overexpression upregulates COX-2 via mitogen-activated kinases/extracellular regulated kinases 1/2 in renal tissues; however, it is not clear whether this effect occurs independently or in concert with AngII type 1 receptor (AT1R) activation. We hypothesized that PRR activation stimulates COX-2 expression independently of AT(1)R in primary cultures of rat renal inner medullary cells. The use of different cell-specific immunomarkers (aquaporin-2 for principal cells, anion exchanger type 1 for intercalated type-A cells, and tenascin C for interstitial cells) and costaining for AT(1)R, COX-2, and PRR revealed that PRR and COX-2 were colocalized in intercalated and interstitial cells whereas principal cells did not express PRR or COX-2. In normal rat kidney sections, PRR and COX-2 were colocalized in intercalated and interstitial cells. In rat renal inner medullary cultured cells, treatment with AngII (100 nmol/L) increased COX-2 expression via AT(1)R. In addition, AngII and rat recombinant prorenin (100 nmol/L) treatments increased extracellular regulated kinases 1/2 phosphorylation, independently. Importantly, rat recombinant prorenin upregulated COX-2 expression in the presence of AT(1)R blockade. Inhibition of mitogen-activated kinases/extracellular regulated kinases 1/2 suppressed COX-2 upregulation mediated by either AngII or rat recombinant prorenin. Furthermore, PRR knockdown using PRR-short hairpin RNA blunted the rat recombinant prorenin-mediated upregulation of COX-2. These results indicate that COX-2 expression is upregulated by activation of either PRR or AT(1)R via mitogen-activated kinases/extracellular regulated kinases 1/2 in rat renal inner medullary cells.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Prostaglandin E-prostanoid4 receptor mediates angiotensin II-induced (pro)renin receptor expression in the rat renal medulla.Hypertension. 2014 Aug;64(2):369-77. doi: 10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.114.03654. Epub 2014 May 27. Hypertension. 2014. PMID: 24866147 Free PMC article.
-
Crosstalk between (Pro)renin receptor and COX-2 in the renal medulla during angiotensin II-induced hypertension.Curr Opin Pharmacol. 2015 Apr;21:89-94. doi: 10.1016/j.coph.2014.12.011. Epub 2015 Feb 12. Curr Opin Pharmacol. 2015. PMID: 25681793 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Glucose promotes the production of interleukine-1beta and cyclooxygenase-2 in mesangial cells via enhanced (Pro)renin receptor expression.Endocrinology. 2009 Dec;150(12):5557-65. doi: 10.1210/en.2009-0442. Epub 2009 Oct 27. Endocrinology. 2009. PMID: 19861503 Free PMC article.
-
Prostaglandin E2 Induces Prorenin-Dependent Activation of (Pro)renin Receptor and Upregulation of Cyclooxygenase-2 in Collecting Duct Cells.Am J Med Sci. 2017 Sep;354(3):310-318. doi: 10.1016/j.amjms.2017.05.018. Epub 2017 May 30. Am J Med Sci. 2017. PMID: 28918839 Free PMC article.
-
The evolving complexity of the collecting duct renin-angiotensin system in hypertension.Nat Rev Nephrol. 2021 Jul;17(7):481-492. doi: 10.1038/s41581-021-00414-6. Epub 2021 Apr 6. Nat Rev Nephrol. 2021. PMID: 33824491 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Renal Denervation Influences Angiotensin II Types 1 and 2 Receptors.Int J Nephrol. 2022 Oct 10;2022:8731357. doi: 10.1155/2022/8731357. eCollection 2022. Int J Nephrol. 2022. PMID: 36262553 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Soluble (Pro)Renin Receptor in Hypertension.Nephron. 2023;147(3-4):234-243. doi: 10.1159/000525635. Epub 2022 Jul 22. Nephron. 2023. PMID: 35871512 Free PMC article. Review.
-
(Pro)renin receptor activation increases profibrotic markers and fibroblast-like phenotype through MAPK-dependent ROS formation in mouse renal collecting duct cells.Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 2017 Nov;44(11):1134-1144. doi: 10.1111/1440-1681.12813. Epub 2017 Aug 30. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 2017. PMID: 28696542 Free PMC article.
-
Prorenin receptor mediates inflammation in renal ischemia.Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 2018 Feb;45(2):133-139. doi: 10.1111/1440-1681.12868. Epub 2017 Nov 22. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 2018. PMID: 28980339 Free PMC article.
-
Role of non-classical renin-angiotensin system axis in renal fibrosis.Front Physiol. 2015 Apr 21;6:117. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2015.00117. eCollection 2015. Front Physiol. 2015. PMID: 25954204 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Ludwig J, Kerscher S, Brandt U, Pfeiffer K, Getlawi F, Apps DK, Schagger H. Identification and characterization of a novel 9.2-kDa membrane sector-associated protein of vacuolar proton-ATPase from chromaffin granules. J Biol Chem. 1998;273:10939–10947. - PubMed
-
- Advani A, Kelly DJ, Cox AJ, White KE, Advani SL, Thai K, Connelly KA, Yuen D, Trogadis J, Herzenberg AM, Kuliszewski MA, Leong-Poi H, Gilbert RE. The (Pro)renin receptor: site-specific and functional linkage to the vacuolar H+-ATPase in the kidney. Hypertension. 2009;542:261–269. - PubMed
-
- Nguyen G, Delarue F, Berrou J, Rondeau E, Sraer JD. Specific receptor binding of renin on human mesangial cells in culture increases plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 antigen. Kidney Int. 1996;50:1897–1903. - PubMed
-
- Nguyen G. Renin//prorenin receptors. Kidney Int. 2006;69:1503–1506. - PubMed
-
- Nguyen G, Contrepas A. Physiology and pharmacology of the (pro)renin receptor. Current Opinion in Pharmacology. 2008;8:127–132. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

