Inhibition of dendritic Ca2+ spikes by GABAB receptors in cortical pyramidal neurons is mediated by a direct Gi/o-β-subunit interaction with Cav1 channels
- PMID: 23184512
- PMCID: PMC3624841
- DOI: 10.1113/jphysiol.2012.245464
Inhibition of dendritic Ca2+ spikes by GABAB receptors in cortical pyramidal neurons is mediated by a direct Gi/o-β-subunit interaction with Cav1 channels
Abstract
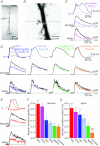
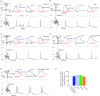
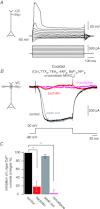
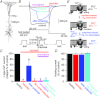
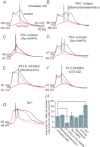
Voltage-dependent calcium channels (VDCCs) serve a wide range of physiological functions and their activity is modulated by different neurotransmitter systems. GABAergic inhibition of VDCCs in neurons has an important impact in controlling transmitter release, neuronal plasticity, gene expression and neuronal excitability. We investigated the molecular signalling mechanisms by which GABA(B) receptors inhibit calcium-mediated electrogenesis (Ca(2+) spikes) in the distal apical dendrite of cortical layer 5 pyramidal neurons. Ca(2+) spikes are the basis of coincidence detection and signal amplification of distal tuft synaptic inputs characteristic for the computational function of cortical pyramidal neurons. By combining dendritic whole-cell recordings with two-photon fluorescence Ca(2+) imaging we found that all subtypes of VDCCs were present in the Ca(2+) spike initiation zone, but that they contribute differently to the initiation and sustaining of dendritic Ca(2+) spikes. Particularly, Ca(v)1 VDCCs are the most abundant VDCC present in this dendritic compartment and they generated the sustained plateau potential characteristic for the Ca(2+) spike. Activation of GABA(B) receptors specifically inhibited Ca(v)1 channels. This inhibition of L-type Ca(2+) currents was transiently relieved by strong depolarization but did not depend on protein kinase activity. Therefore, our findings suggest a novel membrane-delimited interaction of the G(i/o)-βγ-subunit with Ca(v)1 channels identifying this mechanism as the general pathway of GABA(B) receptor-mediated inhibition of VDCCs. Furthermore, the characterization of the contribution of the different VDCCs to the generation of the Ca(2+) spike provides new insights into the molecular mechanism of dendritic computation.
Figures
References
-
- Amitai Y, Friedman A, Connors BW, Gutnick MJ. Regenerative activity in apical dendrites of pyramidal cells in neocortex. Cereb Cortex. 1993;3:26–38. - PubMed
-
- Bettler B, Kaupmann K, Mosbacher J, Gassmann M. Molecular structure and physiological functions of GABAB receptors. Physiol Rev. 2004;84:835–867. - PubMed
-
- Bloodgood BL, Sabatini BL. Nonlinear regulation of unitary synaptic signals by CaV(2.3) voltage-sensitive calcium channels located in dendritic spines. Neuron. 2007;53:249–260. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

