Detecting rare variant effects using extreme phenotype sampling in sequencing association studies
- PMID: 23184518
- PMCID: PMC3601902
- DOI: 10.1002/gepi.21699
Detecting rare variant effects using extreme phenotype sampling in sequencing association studies
Abstract
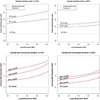
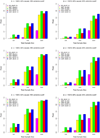
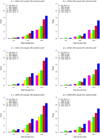
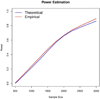
In the increasing number of sequencing studies aimed at identifying rare variants associated with complex traits, the power of the test can be improved by guided sampling procedures. We confirm both analytically and numerically that sampling individuals with extreme phenotypes can enrich the presence of causal rare variants and can therefore lead to an increase in power compared to random sampling. Although application of traditional rare variant association tests to these extreme phenotype samples requires dichotomizing the continuous phenotypes before analysis, the dichotomization procedure can decrease the power by reducing the information in the phenotypes. To avoid this, we propose a novel statistical method based on the optimal Sequence Kernel Association Test that allows us to test for rare variant effects using continuous phenotypes in the analysis of extreme phenotype samples. The increase in power of this method is demonstrated through simulation of a wide range of scenarios as well as in the triglyceride data of the Dallas Heart Study.
© 2012 WILEY PERIODICALS, INC.
Figures
References
-
- Cirulli ET, Goldstein DB. Uncovering the roles of rare variants in common disease through wholegenome sequencing. Nat Rev Genet. 2010;11(6):415–425. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

