Applying ligands profiling using multiple extended electron distribution based field templates and feature trees similarity searching in the discovery of new generation of urea-based antineoplastic kinase inhibitors
- PMID: 23185312
- PMCID: PMC3502486
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0049284
Applying ligands profiling using multiple extended electron distribution based field templates and feature trees similarity searching in the discovery of new generation of urea-based antineoplastic kinase inhibitors
Abstract
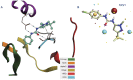
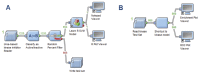
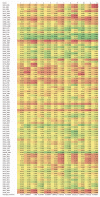
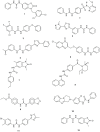
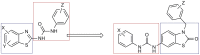
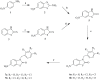
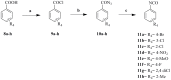
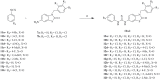
This study provides a comprehensive computational procedure for the discovery of novel urea-based antineoplastic kinase inhibitors while focusing on diversification of both chemotype and selectivity pattern. It presents a systematic structural analysis of the different binding motifs of urea-based kinase inhibitors and the corresponding configurations of the kinase enzymes. The computational model depends on simultaneous application of two protocols. The first protocol applies multiple consecutive validated virtual screening filters including SMARTS, support vector-machine model (ROC = 0.98), Bayesian model (ROC = 0.86) and structure-based pharmacophore filters based on urea-based kinase inhibitors complexes retrieved from literature. This is followed by hits profiling against different extended electron distribution (XED) based field templates representing different kinase targets. The second protocol enables cancericidal activity verification by using the algorithm of feature trees (Ftrees) similarity searching against NCI database. Being a proof-of-concept study, this combined procedure was experimentally validated by its utilization in developing a novel series of urea-based derivatives of strong anticancer activity. This new series is based on 3-benzylbenzo[d]thiazol-2(3H)-one scaffold which has interesting chemical feasibility and wide diversification capability. Antineoplastic activity of this series was assayed in vitro against NCI 60 tumor-cell lines showing very strong inhibition of GI(50) as low as 0.9 uM. Additionally, its mechanism was unleashed using KINEX™ protein kinase microarray-based small molecule inhibitor profiling platform and cell cycle analysis showing a peculiar selectivity pattern against Zap70, c-src, Mink1, csk and MeKK2 kinases. Interestingly, it showed activity on syk kinase confirming the recent studies finding of the high activity of diphenyl urea containing compounds against this kinase. Allover, the new series, which is based on a new kinase scaffold with interesting chemical diversification capabilities, showed that it exhibits its "emergent" properties by perturbing multiple unexplored kinase pathways.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
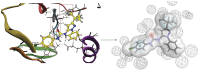
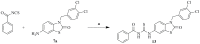
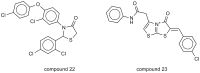
Similar articles
-
Discovery of nitroaryl urea derivatives with antiproliferative properties.J Enzyme Inhib Med Chem. 2016 Aug;31(4):608-18. doi: 10.3109/14756366.2015.1057716. Epub 2015 Jun 26. J Enzyme Inhib Med Chem. 2016. PMID: 26114307
-
Pharmacophore-based virtual screening, synthesis, biological evaluation, and molecular docking study of novel pyrrolizines bearing urea/thiourea moieties with potential cytotoxicity and CDK inhibitory activities.J Enzyme Inhib Med Chem. 2021 Dec;36(1):15-33. doi: 10.1080/14756366.2020.1837124. J Enzyme Inhib Med Chem. 2021. PMID: 33103497 Free PMC article.
-
Anchor-based classification and type-C inhibitors for tyrosine kinases.Sci Rep. 2015 Jun 16;5:10938. doi: 10.1038/srep10938. Sci Rep. 2015. PMID: 26077136 Free PMC article.
-
Spleen tyrosine kinases: biology, therapeutic targets and drugs.Drug Discov Today. 2010 Jul;15(13-14):517-30. doi: 10.1016/j.drudis.2010.05.001. Epub 2010 May 27. Drug Discov Today. 2010. PMID: 20553955 Review.
-
Recent Advances in the Discovery of Multitargeted Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors as Anticancer Agents.ChemMedChem. 2021 Feb 17;16(4):600-620. doi: 10.1002/cmdc.202000658. Epub 2020 Nov 24. ChemMedChem. 2021. PMID: 33179854 Review.
Cited by
-
Computational Approaches: A New Frontier in Cancer Research.Comb Chem High Throughput Screen. 2024;27(13):1861-1876. doi: 10.2174/0113862073265604231106112203. Comb Chem High Throughput Screen. 2024. PMID: 38031782 Review.
References
-
- Li H-Q, Lv P-C, Yan T, Zhu H-L (2009) Urea derivatives as anticancer agents. Anti-Cancer Agents Med Chem 9: 471–480. - PubMed
-
- Dumas J (2002) Protein kinase inhibitors from the urea class. Curr Opin Drug Discovery Dev 5: 718–727. - PubMed
-
- Dumas J, Smith RA, Lowinger TB (2004) Recent developments in the discovery of protein kinase inhibitors from the urea class. Curr Opin Drug Discovery Dev 7: 600–616. - PubMed
-
- Fabian MA, Biggs WH, Treiber DK, Atteridge CE, Azimioara MD, et al. (2005) A small molecule-kinase interaction map for clinical kinase inhibitors. Nat Biotechnol 23: 329–336. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

