Determining vaccination frequency in farmed rainbow trout using Vibrio anguillarum O1 specific serum antibody measurements
- PMID: 23185402
- PMCID: PMC3504153
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0049672
Determining vaccination frequency in farmed rainbow trout using Vibrio anguillarum O1 specific serum antibody measurements
Abstract
Background: Despite vaccination with a commercial vaccine with a documented protective effect against Vibrio anguillarum O1 disease outbreaks caused by this bacterium have been registered among rainbow trout at Danish fish farms. The present study examined specific serum antibody levels as a valid marker for assessing vaccination status in a fish population. For this purpose a highly sensitive enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) was developed and used to evaluate sera from farmed rainbow trout vaccinated against V. anguillarum O1.
Study design: Immune sera from rainbow trout immunised with an experimental vaccine based on inactivated V. anguillarum O1 bacterin in Freund's incomplete adjuvant were used for ELISA optimisation. Subsequently, sera from farmed rainbow trout vaccinated with a commercial vaccine against V. anguillarum were analysed with the ELISA. The measured serum antibody levels were compared with the vaccine status of the fish (vaccinated/unvaccinated) as evaluated through visual examination.
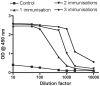
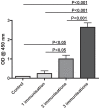
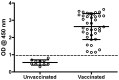
Results: Repeated immunisation with the experimental vaccine lead to increasing levels of specific serum antibodies in the vaccinated rainbow trout. The farmed rainbow trout responded with high antibody levels to a single injection with the commercial vaccine. However, the diversity in responses was more pronounced in the farmed fish. Primary visual examinations for vaccine status in rainbow trout from the commercial farm revealed a large pool of unvaccinated specimens (vaccination failure rate=20%) among the otherwise vaccinated fish. Through serum analyses using the ELISA in a blinded set-up it was possible to separate samples collected from the farmed rainbow trout into vaccinated and unvaccinated fish.
Conclusions: Much attention has been devoted to development of new and more effective vaccines. Here we present a case from a Danish rainbow trout farm indicating that attention should also be directed to the vaccination procedure in order to secure high vaccination frequencies necessary for optimal protection with a reported effective vaccine.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

Similar articles
-
Antigenic variability of Vibrio anguillarum serotype O2a: A hurdle for vaccine efficacy against vibriosis in rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss).Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2022 Dec;131:300-311. doi: 10.1016/j.fsi.2022.09.072. Epub 2022 Oct 3. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2022. PMID: 36202204
-
Improved Protective Efficacy in Rainbow Trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) Against Vibrio anguillarum Through Immunization with a Combination of Formalin-Killed and Auxotrophic-Live V. anguillarum.Mar Biotechnol (NY). 2025 Jan 27;27(1):35. doi: 10.1007/s10126-025-10414-3. Mar Biotechnol (NY). 2025. PMID: 39869218
-
Comparative evaluation of administration methods for a vaccine protecting rainbow trout against Yersinia ruckeri O1 biotype 2 infections.Vet Immunol Immunopathol. 2013 Jul 15;154(1-2):42-7. doi: 10.1016/j.vetimm.2013.04.001. Epub 2013 Apr 8. Vet Immunol Immunopathol. 2013. PMID: 23622778 Clinical Trial.
-
Immunization with viral antigens: infectious pancreatic necrosis.Dev Biol Stand. 1997;90:191-9. Dev Biol Stand. 1997. PMID: 9270848 Review.
-
Immunization with bacterial antigens: Vibrio infections.Dev Biol Stand. 1997;90:93-105. Dev Biol Stand. 1997. PMID: 9270838 Review.
Cited by
-
Approaches towards DNA vaccination against a skin ciliate parasite in fish.PLoS One. 2012;7(11):e48129. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0048129. Epub 2012 Nov 7. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 23144852 Free PMC article.
-
Succinate Promotes Phagocytosis of Monocytes/Macrophages in Teleost Fish.Front Mol Biosci. 2021 Apr 15;8:644957. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2021.644957. eCollection 2021. Front Mol Biosci. 2021. PMID: 33937328 Free PMC article.
-
Assessment of antigenic specificity of polyclonal antisera raised against Avibacterium paragallinarum by ELISA.Vet Anim Sci. 2020 May 16;9:100119. doi: 10.1016/j.vas.2020.100119. eCollection 2020 Jun. Vet Anim Sci. 2020. PMID: 32734120 Free PMC article.
-
A Major QTL for Resistance to Vibrio anguillarum in Rainbow Trout.Front Genet. 2020 Dec 29;11:607558. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2020.607558. eCollection 2020. Front Genet. 2020. PMID: 33447254 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy of Feed-Based Formalin-Killed Vaccine of Streptococcus iniae Stimulates the Gut-Associated Lymphoid Tissues and Immune Response of Red Hybrid Tilapia.Vaccines (Basel). 2021 Jan 14;9(1):51. doi: 10.3390/vaccines9010051. Vaccines (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33466950 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Pedersen K, Skall HF, Lassen-Nielsen AM, Nielsen TF, Henriksen NH, et al. (2008) Surveillance of health status on eight marine rainbow trout, Oncorhynchus mykiss (Walbaum), farms in Denmark in 2006. J Fish Dis 31: 659–667. - PubMed
-
- Hastein T, Gudding R, Evensen O (2005) Bacterial vaccines for fish–an update of the current situation worldwide. Dev Biol (Basel) 121: 55–74. - PubMed
-
- Midtlyng PJ, Reitan LJ, Speilberg L (1996) Experimental studies on the efficacy and side-effects of intraperitoneal vaccination of Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar L) against furunculosis. Fish & Shellfish Immunology 6: 335–350.
-
- Plant KP, Lapatra SE (2011) Advances in fish vaccine delivery. Dev Comp Immunol. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

