Economic burden of human papillomavirus-related diseases in Italy
- PMID: 23185412
- PMCID: PMC3504125
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0049699
Economic burden of human papillomavirus-related diseases in Italy
Erratum in
-
Correction: Economic Burden of Human Papillomavirus-Related Diseases in Italy.PLoS One. 2013 Sep 27;8(9):10.1371/annotation/39ddb7a9-3e7e-4544-a226-2e2b872a5116. doi: 10.1371/annotation/39ddb7a9-3e7e-4544-a226-2e2b872a5116. eCollection 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 24116248 Free PMC article.
Abstract
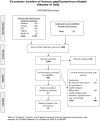
Introduction: Human papilloma virus (HPV) genotypes 6, 11, 16, and 18 impose a substantial burden of direct costs on the Italian National Health Service that has never been quantified fully. The main objective of the present study was to address this gap: (1) by estimating the total direct medical costs associated with nine major HPV-related diseases, namely invasive cervical cancer, cervical dysplasia, cancer of the vulva, vagina, anus, penis, and head and neck, anogenital warts, and recurrent respiratory papillomatosis, and (2) by providing an aggregate measure of the total economic burden attributable to HPV 6, 11, 16, and 18 infection.
Methods: For each of the nine conditions, we used available Italian secondary data to estimate the lifetime cost per case, the number of incident cases of each disease, the total economic burden, and the relative prevalence of HPV types 6, 11, 16, and 18, in order to estimate the aggregate fraction of the total economic burden attributable to HPV infection.
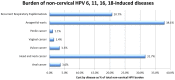
Results: The total direct costs (expressed in 2011 Euro) associated with the annual incident cases of the nine HPV-related conditions included in the analysis were estimated to be €528.6 million, with a plausible range of €480.1-686.2 million. The fraction attributable to HPV 6, 11, 16, and 18 was €291.0 (range €274.5-315.7 million), accounting for approximately 55% of the total annual burden of HPV-related disease in Italy.
Conclusions: The results provided a plausible estimate of the significant economic burden imposed by the most prevalent HPV-related diseases on the Italian welfare system. The fraction of the total direct lifetime costs attributable to HPV 6, 11, 16, and 18 infections, and the economic burden of noncervical HPV-related diseases carried by men, were found to be cost drivers relevant to the making of informed decisions about future investments in programmes of HPV prevention.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
-
- Wiley DA, Mansongsong E (2006) Human papillomavirus: the burden of infection. Obstet Gynecol Surv 61: S3–S14. - PubMed
-
- Walboomers JM, Jacobs MV, Manos MM, Bosch FX, Kummer JA, et al. (1999) Human papillomavirus is a necessary cause of invasive cervical cancer worldwide. J Pathol 189(1): 12–9. - PubMed
-
- Chaturvedi AK (2010) Beyond cervical cancer: burden of other HPV-related cancers among men and women. Journal of Adolescent Health 46: S20–S26. - PubMed
-
- Koutsky LA, Galloway DA, Holmes KK (1988) Epidemiology of genital human papillomavirus infection. Epidemiol Rev 10: 122–163. - PubMed

