Nicotine uses neuron-glia communication to enhance hippocampal synaptic transmission and long-term memory
- PMID: 23185511
- PMCID: PMC3503711
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0049998
Nicotine uses neuron-glia communication to enhance hippocampal synaptic transmission and long-term memory
Abstract
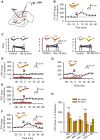
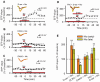
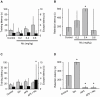
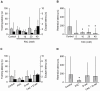
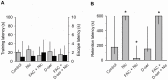
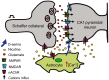
Nicotine enhances synaptic transmission and facilitates long-term memory. Now it is known that bi-directional glia-neuron interactions play important roles in the physiology of the brain. However, the involvement of glial cells in the effects of nicotine has not been considered until now. In particular, the gliotransmitter D-serine, an endogenous co-agonist of NMDA receptors, enables different types of synaptic plasticity and memory in the hippocampus. Here, we report that hippocampal long-term synaptic plasticity induced by nicotine was annulled by an enzyme that degrades endogenous D-serine, or by an NMDA receptor antagonist that acts at the D-serine binding site. Accordingly, both effects of nicotine: the enhancement of synaptic transmission and facilitation of long-term memory were eliminated by impairing glial cells with fluoroacetate, and were restored with exogenous D-serine. Together, these results show that glial D-serine is essential for the long-term effects of nicotine on synaptic plasticity and memory, and they highlight the roles of glial cells as key participants in brain functions.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Bell-shaped D-serine actions on hippocampal long-term depression and spatial memory retrieval.Cereb Cortex. 2008 Oct;18(10):2391-401. doi: 10.1093/cercor/bhn008. Epub 2008 Feb 14. Cereb Cortex. 2008. PMID: 18281302
-
Reparatory effects of nicotine on NMDA receptor-mediated synaptic plasticity in the hippocampal CA1 region of chronically lead-exposed rats.Eur J Neurosci. 2006 Mar;23(5):1111-9. doi: 10.1111/j.1460-9568.2006.04645.x. Eur J Neurosci. 2006. PMID: 16553775
-
Bidirectional synaptic plasticity induced by conditioned stimulations with different number of pulse at hippocampal CA1 synapses: roles of N-methyl-D-aspartate and metabotropic glutamate receptors.Synapse. 2011 Aug;65(8):795-803. doi: 10.1002/syn.20906. Epub 2011 Mar 10. Synapse. 2011. PMID: 21218453
-
Plasticity, hippocampal place cells, and cognitive maps.Arch Neurol. 2001 Jun;58(6):874-81. doi: 10.1001/archneur.58.6.874. Arch Neurol. 2001. PMID: 11405801 Review.
-
Hippocampal long-term synaptic plasticity and signal amplification of NMDA receptors.Crit Rev Neurobiol. 2006;18(1-2):71-84. doi: 10.1615/critrevneurobiol.v18.i1-2.80. Crit Rev Neurobiol. 2006. PMID: 17725510 Review.
Cited by
-
Potential of Glial Cell Modulators in the Management of Substance Use Disorders.CNS Drugs. 2020 Jul;34(7):697-722. doi: 10.1007/s40263-020-00721-9. CNS Drugs. 2020. PMID: 32246400 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Astrocyte Calcium Responses to Sensory Input: Influence of Circuit Organization and Experimental Factors.Front Neural Circuits. 2017 Mar 22;11:16. doi: 10.3389/fncir.2017.00016. eCollection 2017. Front Neural Circuits. 2017. PMID: 28381991 Free PMC article. Review. No abstract available.
-
Gene expression profiling of midbrain dopamine neurons upon gestational nicotine exposure.Med Biol Eng Comput. 2017 Mar;55(3):467-482. doi: 10.1007/s11517-016-1531-8. Epub 2016 Jun 2. Med Biol Eng Comput. 2017. PMID: 27255453
-
Glial cells as therapeutic targets for smoking cessation.Neuropharmacology. 2020 Sep 15;175:108157. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2020.108157. Epub 2020 May 24. Neuropharmacology. 2020. PMID: 32461156 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Molecular Insights Into Memory-Enhancing Metabolites of Nicotine in Brain: A Systematic Review.Front Neurosci. 2019 Jan 15;12:1002. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2018.01002. eCollection 2018. Front Neurosci. 2019. PMID: 30697142 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ben Achour S, Pascual O (2010) Glia: the many ways to modulate synaptic plasticity. Neurochem Int 57: 440–445. - PubMed
-
- Perea G, Araque A (2010) GLIA modulates synaptic transmission. Brain Res Rev 63: 93–102. - PubMed
-
- Magistretti PJ (2006) Neuron-glia metabolic coupling and plasticity. J Exp Biol 209: 2304–2311. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

