Omeprazole blocks STAT6 binding to the eotaxin-3 promoter in eosinophilic esophagitis cells
- PMID: 23185525
- PMCID: PMC3503709
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0050037
Omeprazole blocks STAT6 binding to the eotaxin-3 promoter in eosinophilic esophagitis cells
Abstract
Background: Patients who have esophageal eosinophilia without gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) nevertheless can respond to proton pump inhibitors (PPIs), which can have anti-inflammatory actions independent of effects on gastric acid secretion. In esophageal cell cultures, omeprazole has been reported to inhibit Th2 cytokine-stimulated expression of eotaxin-3, an eosinophil chemoattractant contributing to esophageal eosinophilia in eosinophilic esophagitis (EoE). The objective of this study was to elucidate molecular mechanisms underlying PPI inhibition of IL-4-stimulated eotaxin-3 production by esophageal cells.
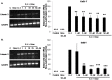
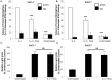
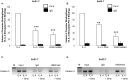
Methods/findings: Telomerase-immortalized and primary cultures of esophageal squamous cells from EoE patients were treated with IL-4 in the presence or absence of acid-activated omeprazole or lansoprazole. We measured eotaxin-3 protein secretion by ELISA, mRNA expression by PCR, STAT6 phosphorylation and nuclear translocation by Western blotting, eotaxin-3 promoter activation by an exogenous reporter construct, and STAT6, RNA polymerase II, and trimethylated H3K4 binding to the endogenous eotaxin-3 promoter by ChIP assay. Omeprazole in concentrations ≥5 µM significantly decreased IL-4-stimulated eotaxin-3 protein secretion and mRNA expression. Lansoprazole also blocked eotaxin-3 protein secretion. Omeprazole had no effect on eotaxin-3 mRNA stability or on STAT6 phosphorylation and STAT6 nuclear translocation. Rather, omeprazole blocked binding of IL-4-stimulated STAT6, RNA polymerase II, and trimethylated H3K4 to the eotaxin-3 promoter.
Conclusions/significance: PPIs, in concentrations achieved in blood with conventional dosing, significantly inhibit IL-4-stimulated eotaxin-3 expression in EoE esophageal cells and block STAT6 binding to the promoter. These findings elucidate molecular mechanisms whereby patients with Th2 cytokine-driven esophageal eosinophilia can respond to PPIs, independent of effects on gastric acid secretion.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures




Similar articles
-
JAK-STAT6 Pathway Inhibitors Block Eotaxin-3 Secretion by Epithelial Cells and Fibroblasts from Esophageal Eosinophilia Patients: Promising Agents to Improve Inflammation and Prevent Fibrosis in EoE.PLoS One. 2016 Jun 16;11(6):e0157376. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0157376. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 27310888 Free PMC article.
-
Omeprazole blocks eotaxin-3 expression by oesophageal squamous cells from patients with eosinophilic oesophagitis and GORD.Gut. 2013 Jun;62(6):824-32. doi: 10.1136/gutjnl-2012-302250. Epub 2012 May 12. Gut. 2013. PMID: 22580413 Free PMC article.
-
Proton pump inhibitors decrease eotaxin-3 expression in the proximal esophagus of children with esophageal eosinophilia.PLoS One. 2014 Jul 2;9(7):e101391. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0101391. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 24988451 Free PMC article.
-
Proton pump inhibitor-responsive oesophageal eosinophilia and eosinophilic oesophagitis: more similarities than differences.Curr Opin Gastroenterol. 2015 Jul;31(4):309-15. doi: 10.1097/MOG.0000000000000185. Curr Opin Gastroenterol. 2015. PMID: 26039722 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Proton-pump inhibitor-responsive esophageal eosinophilia.Curr Opin Gastroenterol. 2014 Jul;30(4):428-33. doi: 10.1097/MOG.0000000000000080. Curr Opin Gastroenterol. 2014. PMID: 24837227 Review.
Cited by
-
Overlapping Transcriptional Profile in Proton Pump Inhibitor Responsive and Nonresponsive Eosinophilic Esophagitis.Clin Transl Gastroenterol. 2022 Nov 1;13(11):e00540. doi: 10.14309/ctg.0000000000000540. Clin Transl Gastroenterol. 2022. PMID: 36201660 Free PMC article.
-
Eosinophilic esophagitis in adults: An update.World J Gastrointest Pharmacol Ther. 2016 May 6;7(2):207-13. doi: 10.4292/wjgpt.v7.i2.207. World J Gastrointest Pharmacol Ther. 2016. PMID: 27158535 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Eosinophilic oesophagitis: clinical presentation and pathogenesis.Postgrad Med J. 2014 May;90(1063):282-9. doi: 10.1136/postgradmedj-2012-131403. Epub 2014 Mar 19. Postgrad Med J. 2014. PMID: 24647582 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Emerging therapeutic strategies for eosinophilic esophagitis.Curr Treat Options Gastroenterol. 2014 Mar;12(1):1-17. doi: 10.1007/s11938-013-0001-8. Curr Treat Options Gastroenterol. 2014. PMID: 24370990
-
Biological therapies for eosinophilic gastrointestinal diseases.J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2018 Jul;142(1):24-31.e2. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2018.05.018. Epub 2018 May 31. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2018. PMID: 29859203 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Kahrilas PJ, Shaheen NJ, Vaezi MF (2008) American Gastroenterological Association Institute technical review on the management of gastroesophageal reflux disease. Gastroenterology, 135, 1392–1413, 1413. - PubMed
-
- Moayyedi P, Soo S, Deeks J, Delaney B, Innes M, et al... (2006) Pharmacological interventions for non-ulcer dyspepsia. Cochrane. Database. Syst. Rev., CD001960. - PubMed
-
- Kahrilas PJ, Hughes N, Howden CW (2011) Response of unexplained chest pain to proton pump inhibitor treatment in patients with and without objective evidence of gastro-oesophageal reflux disease. Gut, 60, 1473–1478. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

